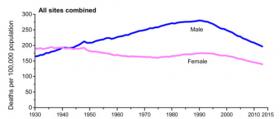
The report estimates that there will be 1,735,350 new cancer cases and 609,640 cancer deaths in the United States in 2018*. The cancer death rate dropped 26% from its peak of 215.1 per 100,000 population in 1991 to 158.6 per 100,000 in 2015. A significant proportion of the drop is due to steady reductions in smoking and advances in early detection and treatment. The overall decline is driven by decreasing death rates for the four major cancer sites: Lung (declined 45% from 1990 to 2015 among men and 19% from 2002 to 2015 among women); female breast (down 39% from 1989 to 2015), prostate (down 52% from 1993 to 2015), and colorectal (down 52% from 1970 to 2015).
The report estimates that there will be 1,735,350 new cancer cases and 609,640 cancer deaths in the United States in 2018*. The cancer death rate dropped 26% from its peak of 215.1 per 100,000 population in 1991 to 158.6 per 100,000 in 2015. A significant proportion of the drop is due to steady reductions in smoking and advances in early detection and treatment. The overall decline is driven by decreasing death rates for the four major cancer sites: Lung (declined 45% from 1990 to 2015 among men and 19% from 2002 to 2015 among women); female breast (down 39% from 1989 to 2015), prostate (down 52% from 1993 to 2015), and colorectal (down 52% from 1970 to 2015).
Continue reading at American Cancer Society
Image: The cancer death rate dropped 1.7% from 2014 to 2015, continuing a drop that began in 1991 and has reached 26%, resulting in nearly 2.4 million fewer cancer deaths during that time.
Source: The data is reported in Cancer Statistics 2018, the American Cancer Society’s comprehensive annual report on cancer incidence, mortality, and survival. It is published in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians and is accompanied by its consumer version: Cancer Facts and Figures 2018.