
After long-awaited snowfall in January, parts of the Alps are now covered with fresh powder and happy skiers. But the Swiss side of the iconic mountain range had the driest December since record-keeping began over 150 years ago, and 2016 was the third year in a row with scarce snow over the Christmas period. A study published today in The Cryosphere, a journal of the European Geosciences Union, shows bare Alpine slopes could be a much more common sight in the future.
>> Read the Full Article

A novel air quality model will help air quality forecasters predict surface ozone levels up to 48-hours in advance and with fewer resources, according to a team of meteorologists.
The method, called regression in self-organizing map (REGiS), weighs and combines statistical air quality models by pairing them with predicted weather patterns to create probabilistic ozone forecasts. Unlike current chemical transport models, REGiS can predict ozone levels up to 48 hours in advance without requiring significant computational power.
>> Read the Full Article

Researchers have completed the first flights of a NASA-led field campaign that is targeting one of the biggest gaps in scientists' understanding of Earth's water resources: snow.
NASA uses the vantage point of space to study all aspects of Earth as an interconnected system. But there remain significant obstacles to measuring accurately how much water is stored across the planet's snow-covered regions. The amount of water in snow plays a major role in water availability for drinking water, agriculture and hydropower.
>> Read the Full Article
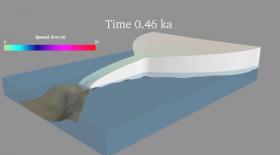
New findings from the University of Michigan explain an Ice Age paradox and add to the mounting evidence that climate change could bring higher seas than most models predict.
The study, published in Nature, shows how small spikes in the temperature of the ocean, rather than the air, likely drove the rapid disintegration cycles of the expansive ice sheet that once covered much of North America.
>> Read the Full Article

The tenth SpaceX cargo resupply launch to the International Space Station, targeted for launch Feb. 18, will deliver investigations that study human health, Earth science and weather patterns. Here are some highlights of the research headed to the orbiting laboratory:
Crystal growth investigation could improve drug delivery, manufacturing
Monoclonal antibodies are important for fighting off a wide range of human diseases, including cancers. These antibodies work with the natural immune system to bind to certain molecules to detect, purify and block their growth. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS PCG 5) investigation will crystallize a human monoclonal antibody, developed by Merck Research Labs, that is currently undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of immunological disease.
>> Read the Full Article

In order to restore tropical rainforests, it is not enough to simply set up protected areas and leave them to their own devices. In particular, tree species with large fruit and seeds distributed by birds will have to be actively planted. This is one of the conclusions of a large-scale study by scientists from ETH Zurich in the Western Ghats, the mountain range running along the western coast of India. Today, the rainforest that exists there is highly fragmented. In the late 20th century in particular, large areas fell victim to intensive logging and commercial agriculture such as coffee and tea plantations.
>> Read the Full Article

Savannahs form one of the largest habitats in the world, covering around one-fifth of the Earth's land area. They are mainly to be found in sub-Saharan Africa. Savannahs are home not only to unique wildlife, including the 'Big Five' - the African elephant, rhinoceros, Cape buffalo, leopard and lion - but also to thousands of endemic plant species such as the baobab, or monkey bread tree.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment