
Daily Arctic sea ice extents for May 2016 tracked two to four weeks ahead of levels seen in 2012, which had the lowest September extent in the satellite record. Current sea ice extent numbers are tentative due to the preliminary nature of the DMSP F-18 satellite data, but are supported by other data sources. An unusually early retreat of sea ice in the Beaufort Sea and pulses of warm air entering the Arctic from eastern Siberia and northernmost Europe are in part driving below-average ice conditions. Snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere was the lowest in fifty years for April and the fourth lowest for May. Antarctic sea ice extent grew slowly during the austral autumn and was below average for most of May.
>> Read the Full Article

If the U.S. healthcare system were a country, it would rank 13th in the world for greenhouse gas emissions, according to new research. The study, published June 9 in PLOS ONE, quantified previously unreported environmental and public health impacts of the nation's healthcare sector.
>> Read the Full Article

An international team of scientists have found a potentially viable way to remove anthropogenic (caused or influenced by humans) carbon dioxide emissions from the atmosphere - turn it into rock.
The study, published today in Science, has shown for the first time that the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) can be permanently and rapidly locked away from the atmosphere, by injecting it into volcanic bedrock. The CO2 reacts with the surrounding rock, forming environmentally benign minerals.
>> Read the Full Article

A new report confirms that 2015 was a record-breaking year for renewable energy in which 147 Gigawatts of renewable electricity came online.
That figure represents the largest annual increase ever recorded, and is due in part to the $286 billion invested in renewables. In fact, in 2015 almost twice as much money was spent on renewable energy, like solar and wind power, than fossil fuels like gas-fired power stations — only $130 billion.
This information comes as part of the Renewables Global Status Report authored by the global renewable energy policy network known as REN21.
>> Read the Full Article
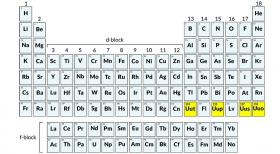
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) Inorganic Chemistry Division has published a Provisional Recommendation for the names and symbols of the recently discovered superheavy elements 113, 115, 117, and 118.
The provisional names for 115, 117 and 118 -- originally proposed by the discovering team from the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia; the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, California; and Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee -- will now undergo a statutory period for public review before the names and symbols can be finally approved by the IUPAC Council.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment