
Three researchers at the University of Regina have been awarded a provincial research grant to study the role of agricultural dugouts in greenhouse gas capture.
Dr. Kerri Finlay, Dr. Peter Leavitt, Dr. Gavin Simpson of the biology department, along with Dr. Helen Baulch of the University of Saskatchewan, were recently awarded $255,030 from the Saskatchewan Ministry of Agriculture's Agriculture Development Fund.
>> Read the Full Article
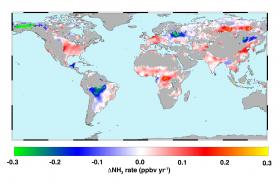
The first global, long-term satellite study of airborne ammonia gas has revealed “hotspots” of the pollutant over four of the world’s most productive agricultural regions. The results of the study, conducted using data from NASA’s Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on NASA’s Aqua satellite, could inform the development of strategies to control pollution from ammonia and ammonia byproducts in Earth’s agricultural areas.
A University of Maryland-led team discovered steadily increasing ammonia concentrations from 2002 to 2016 over agricultural centers in the United States, Europe, China and India. Increased concentrations of atmospheric ammonia are linked to poor air and water quality.
>> Read the Full Article
The oceans are great at absorbing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air, but when their deep waters are brought to the surface, the oceans themselves can be a source of this prevalent greenhouse gas.
Wind patterns together with the Earth’s rotation drive deep ocean water — and the CO2 it sequesters — upward, replacing surface water moving offshore. A process known as upwelling, it occurs on the west coasts of continents. And it’s part of a never-ending loop in which CO2 levels in the surface ocean rise and fall in a natural rhythm.
>> Read the Full Article

With the first day of spring around the corner, temperatures are beginning to rise, ice is melting, and the world around us is starting to blossom. Scientists sometimes refer to this transition from winter to the growing season as the “vernal window,” and a new study led by the University of New Hampshire shows this window may be opening earlier and possibly for longer.
“Historically, the transition into spring is comparatively shorter than other seasons,” said Alexandra Contosta, a research assistant professor at the University of New Hampshire’s Earth Systems Research Center. “You have snow melting and lots of water moving through aquatic systems, nutrients flushing through that water, soils warming up, and buds breaking on trees. Something striking happens after a very cold winter or when there’s been a lot of snow. Things seem to wake up all together, which is why spring seems to happen so quickly and can feel so dramatic.”
>> Read the Full Article

Measures such as river restoration and tree planting aim to restore processes that have been affected by human activities like farming, land management and house-building. Natural flood management is an area of increasing interest for policy makers, but its implementation can present a complex balancing act between the needs of different groups, including the public, farmers and land owners. Mixed messages about their effectiveness and the scale needed to implement natural flood management measures successfully add to the uncertainty surrounding their benefits. Now a team of experts, led by Dr Simon Dadson of the School of Geography and the Environment at the University of Oxford, has compiled evidence on natural flood management to inform policy decision-making and show where there are still crucial gaps in knowledge. The article shines a light on the scientific evidence available from a variety of sources, ranging from field data to model projections and expert opinion.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment