
Bringing renewable power ‘by wire’ from western China to its power-hungry Eastern cities could have benefits for both local air quality and global climate change, new research has found.
The study, published today in the journal Environmental Research Letters, examined if ongoing power transmission capacity investment in China – driven largely by concerns over air pollution – could also reduce local adverse health impacts from air pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
>> Read the Full Article
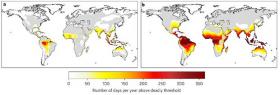
Seventy-four percent of the world’s population will be exposed to deadly heatwaves by 2100 if carbon gas emissions continue to rise at current rates, according to a study published in Nature Climate Change. Even if emissions are aggressively reduced, the percent of the world’s human population affected is expected to reach 48 percent.
“We are running out of choices for the future,” said Camilo Mora, associate professor of geography in the College of Social Sciences at the University of Hawai?i at M?noa and lead author of the study. “For heatwaves, our options are now between bad or terrible. Many people around the world are already paying the ultimate price of heatwaves, and while models suggest that this is likely to continue, it could be much worse if emissions are not considerably reduced. The human body can only function within a narrow range of core body temperatures around 37°C. Heatwaves pose a considerable risk to human life because hot weather, aggravated with high humidity, can raise body temperature, leading to life threatening conditions.”
>> Read the Full Article

Today’s soybeans are typically golden yellow, with a tiny blackish mark where they attach to the pod. In a field of millions of beans, nearly all of them will have this look. Occasionally, however, a bean will turn up half-black, with a saddle pattern similar to a black-eyed pea.
>> Read the Full Article

Astronomers have released an image of a vast filament of star-forming gas, 1,200 light-years away, in the stellar nursery of the Orion Nebula.
The image shows ammonia molecules within a 50-light-year long filament detected through radio observations made with the Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope in West Virginia. It accompanies the first release of results from a research collaboration published in the Astrophysical Journal Supplement.
>> Read the Full Article

The anxiety over antibiotic-resistant superbugs, which are responsible for 23,000 deaths a year in the United States, is likely to grow in California, following the recent discovery by UCLA researchers of high levels of antibiotic-resistant genes in parks in four cities.
Antibiotic-resistant genes, or ARGs, lead to antibiotic-resistant bacteria. And with antibiotic resistance rapidly increasing, worldwide they are expected to kill 10 million people annually by 2050 — more than cancer.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment