
Mercury is a powerful poison. It can cause brain damage, tremors, paralysis and death.
But two researchers at the University of Ottawa’s Department of Biology have found a way to neutralize this toxic metal by pitting it against a small but mighty foe — a group of microorganisms known as purple non-sulphur bacteria.
>> Read the Full Article

A new study by scientists at the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science’s Chesapeake Biological Laboratory, Cornell University and Duke University is the first in a series to understand how marine mammals like porpoises, whales, and dolphins may be affected by the construction of wind farms off the coast of Maryland. The new research offers insight into previously unknown habits of harbor porpoises in the Maryland Wind Energy Area, a 125-square-mile area off the coast of Ocean City that may be the nation’s first commercial-scale offshore wind farm.
>> Read the Full Article

A new analysis of 15 years of NASA satellite cloud measurements finds that clouds worldwide show no definitive trend during this period toward decreasing or increasing in height. The new study updates an earlier analysis of the first 10 years of the same data that suggested cloud heights might be getting lower.
Clouds are both Earth's cooling sunshade and its insulating blanket. Currently their cooling effect prevails globally. But as Earth warms, the characteristics of clouds over different global regions -- their thickness, brightness and height -- are expected to change in ways that scientists don't fully understand. These changes could either amplify warming or slow it. Pinning down some of the uncertainties around clouds is one of the biggest challenges in determining the future rate of global climate change.
>> Read the Full Article

Researchers at the Yale School of Public Health and Peking University have found that Chinese families are willing to invest up to 6 percent of their annual income in efforts to improve air quality.
Published in Ecological Economics on March 7, the study aimed to determine the amount people are willing to pay for efforts to reduce air pollution, such as environmental policies to introduce more electric cars and natural gas heating. The researchers found that on average, families with children under the age of 6 are willing to invest 5.9 percent of their annual income, while families without children under 6 years old are willing to pay 3.3 percent.
>> Read the Full Article
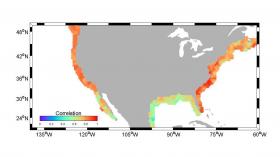
Thanks in large part to satellite measurements, scientists' skill in measuring how much sea levels are rising on a global scale - currently 0.13 inch (3.4 millimeters) per year - has improved dramatically over the past quarter century. But at the local level, it's been harder to estimate specific regional sea level changes 10 or 20 years away - the critical timeframe for regional planners and decision makers.
That's because sea level changes for many reasons, on differing timescales, and is not the same from one place to the next. Developing more accurate regional forecasts of sea level rise will therefore have far-reaching benefits for the more than 30 percent of Americans who currently reside along the Pacific, Atlantic or Gulf Coasts of the contiguous United States.
>> Read the Full Article
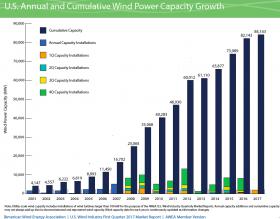
The U.S. wind energy industry experienced its fastest first-quarter growth since 2009, installing 2,000 new megawatts of capacity — enough to power about 500,000 homes — on its way to producing 5.5 percent of the country’s electricity.
The American Wind Energy Association (AWEA) also reported that another 21,000 megawatts of wind energy capacity is now under construction or in advanced development — enough to power an additional 5 million average U.S. homes. The AWEA said that 908 utility-scale wind turbines were erected in the first quarter of 2017, driving a nearly four-fold increase in wind energy growth over the first quarter of 2016. Forty-one U.S. states — most recently Rhode Island and North Carolina — now have utility-scale wind power projects. Texas is by far the wind energy leader in the U.S., with a wind power capacity of 21,000 megawatts.
>> Read the Full Article

Expanding its work in renewable energy, the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) is launching a three-year project to develop specialized forecasts for a major wind and solar energy facility in Kuwait.
"We're putting our expertise and technology to work around the world," said NCAR Senior Scientist Sue Ellen Haupt, the principal investigator on the project. "This landmark project meets our mission of science in service to society."
>> Read the Full Article
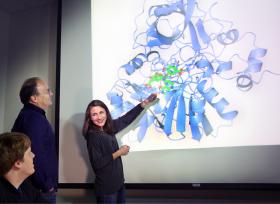
A recent discovery by Sandia National Laboratories researchers may unlock the potential of biofuel waste — and ultimately make biofuels competitive with petroleum.
Fuel made from plants is much more expensive than petroleum, but one way to decrease the cost would be to sell products made from lignin, the plant waste left over from biofuel production.
Lignin typically is either burned to produce electricity or left unused in piles because no one has yet determined how to convert it into useful products, such as renewable plastics, fabrics, nylon and adhesives. The electricity isn’t even available to the general public; it’s only used by companies that create large amounts of lignin, like pulp and paper manufacturers. Now Sandia scientists, working with researchers from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory at the Joint BioEnergy Institute, have decoded the structure and behavior of LigM, an enzyme that breaks down molecules derived from lignin.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment