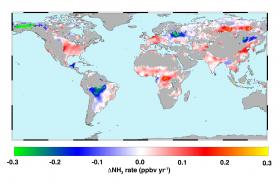
The first global, long-term satellite study of airborne ammonia gas has revealed “hotspots” of the pollutant over four of the world’s most productive agricultural regions. The results of the study, conducted using data from NASA’s Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on NASA’s Aqua satellite, could inform the development of strategies to control pollution from ammonia and ammonia byproducts in Earth’s agricultural areas.
A University of Maryland-led team discovered steadily increasing ammonia concentrations from 2002 to 2016 over agricultural centers in the United States, Europe, China and India. Increased concentrations of atmospheric ammonia are linked to poor air and water quality.
>> Read the Full Article
The oceans are great at absorbing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air, but when their deep waters are brought to the surface, the oceans themselves can be a source of this prevalent greenhouse gas.
Wind patterns together with the Earth’s rotation drive deep ocean water — and the CO2 it sequesters — upward, replacing surface water moving offshore. A process known as upwelling, it occurs on the west coasts of continents. And it’s part of a never-ending loop in which CO2 levels in the surface ocean rise and fall in a natural rhythm.
>> Read the Full Article

With the first day of spring around the corner, temperatures are beginning to rise, ice is melting, and the world around us is starting to blossom. Scientists sometimes refer to this transition from winter to the growing season as the “vernal window,” and a new study led by the University of New Hampshire shows this window may be opening earlier and possibly for longer.
“Historically, the transition into spring is comparatively shorter than other seasons,” said Alexandra Contosta, a research assistant professor at the University of New Hampshire’s Earth Systems Research Center. “You have snow melting and lots of water moving through aquatic systems, nutrients flushing through that water, soils warming up, and buds breaking on trees. Something striking happens after a very cold winter or when there’s been a lot of snow. Things seem to wake up all together, which is why spring seems to happen so quickly and can feel so dramatic.”
>> Read the Full Article

Measures such as river restoration and tree planting aim to restore processes that have been affected by human activities like farming, land management and house-building. Natural flood management is an area of increasing interest for policy makers, but its implementation can present a complex balancing act between the needs of different groups, including the public, farmers and land owners. Mixed messages about their effectiveness and the scale needed to implement natural flood management measures successfully add to the uncertainty surrounding their benefits. Now a team of experts, led by Dr Simon Dadson of the School of Geography and the Environment at the University of Oxford, has compiled evidence on natural flood management to inform policy decision-making and show where there are still crucial gaps in knowledge. The article shines a light on the scientific evidence available from a variety of sources, ranging from field data to model projections and expert opinion.
>> Read the Full Article

Plants possess molecular mechanisms that prevent them from blooming in winter. Once the cold of win-ter has passed, they are deactivated. However, if it is still too cold in spring, plants adapt their blooming behavior accordingly. Scientists from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have discovered genetic changes for this adaptive behavior. In light of the temperature changes resulting from climate change, this may come in useful for securing the production of food in the future.
>> Read the Full Article

Using biofuels to help power jet engines reduces particle emissions in their exhaust by as much as 50 to 70 percent, in a new study conclusion that bodes well for airline economics and Earth’s environment.
The findings are the result of a cooperative international research program led by NASA and involving agencies from Germany and Canada, and are detailed in a study published in the journal Nature.
>> Read the Full Article

At University of Toronto Mississauga, a plastic tower sprouts produce including curly starbor kale, buttercrunch and collard greens.
Rising almost six feet off the ground and illuminated by high output fluorescent bulbs, the indoor farm wall grows plants hydroponically – with nutrient solution, instead of soil. The water nourishes the roots, collects in a gutter and then recirculates back to a nutrient tank that feeds back into the hydroponic system.
>> Read the Full Article

You are what you eat, as the saying goes, and while good dietary choices boost your own health, they also could improve the health care system and even benefit the planet. Healthier people mean not only less disease but also reduced greenhouse gas emissions from health care. As it turns out, some relatively small diet tweaks could add up to significant inroads in addressing climate change.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment