
Successful trials of CharIoT, a unique new system that simultaneously records temperature, humidity and energy use in the home, have opened the way for low-income households to save money while reducing risks to their health.
Harnessing Internet of Things technology, the system generates easy-to-use data that can help local authorities, housing associations, energy suppliers, health authorities and others to target and tailor the energy advice they give to vulnerable people.
As well as revealing under- or over-heated parts of a home, CharIoT enables energy advisors to pinpoint where and why damp or mould may pose a problem. They can then suggest, for example, ways of using heaters more efficiently and cost-effectively, blocking draughts and eliminating dampness through better ventilation.
>> Read the Full Article

The effects of climate change will likely cause smaller but stronger storms in the United States, according to a new framework for modeling storm behavior developed at the University of Chicago and Argonne National Laboratory. Though storm intensity is expected to increase over today’s levels, the predicted reduction in storm size may alleviate some fears of widespread severe flooding in the future.
The new approach, published today in Journal of Climate, uses new statistical methods to identify and track storm features in both observational weather data and new high-resolution climate modeling simulations. When applied to one simulation of the future effects of elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide, the framework helped clarify a common discrepancy in model forecasts of precipitation changes.
>> Read the Full Article

A new study predicts that warming temperatures will contribute to the release into the atmosphere of carbon that has long been locked up securely in the coldest reaches of our planet.
Soil and climate expert Katherine Todd-Brown, a scientist at the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, is an author of the paper, published in the Dec. 1 issue of the journal Nature, which draws upon data collected through 49 separate field experiments around the world.
The research was led by Thomas Crowther, formerly of Yale and now at the Netherlands Institute of Ecology, and colleague Mark Bradford at Yale. Scientists from more than 30 institutions across the globe, including PNNL, collaborated on the study.
>> Read the Full Article

Tornadoes and severe thunderstorms kill people and damage property every year. Estimated U.S. insured losses due to severe thunderstorms in the first half of 2016 were $8.5 billion. The largest U.S. impacts of tornadoes result from tornado outbreaks, sequences of tornadoes that occur in close succession. Last spring a research team led by Michael Tippett, associate professor of applied physics and applied mathematics at Columbia Engineering, published a study showing that the average number of tornadoes during outbreaks—large-scale weather events that can last one to three days and span huge regions—has risen since 1954. But they were not sure why.
In a new paper, published December 1 in Science via First Release, the researchers looked at increasing trends in the severity of tornado outbreaks where they measured severity by the number of tornadoes per outbreak. They found that these trends are increasing fastest for the most extreme outbreaks. While they saw changes in meteorological quantities that are consistent with these upward trends, the meteorological trends were not the ones expected under climate change.
>> Read the Full Article

Coral genotypes can survive for thousands of years, possibly making them the longest-lived animals in the world, according to researchers at Penn State, the National Marine Fisheries Service and Dial Cordy & Associates.
The team recently determined the ages of elkhorn corals — Acropora palmata — in Florida and the Caribbean and estimated the oldest genotypes to be over 5,000 years old. The results are useful for understanding how corals will respond to current and future environmental change.
>> Read the Full Article

March 2012 was unusually warm. Biomass crops around the Midwest were well established and thriving. But when a late frost came in mid-April, all of that changed.
“When I went out in the morning, I was just shocked,” says University of Illinois agronomist D.K. Lee. “All the grasses were covered in frost. By noon, Miscanthus and switchgrass had turned black. The only plant that was untouched was prairie cordgrass.”
>> Read the Full Article

Whether intentionally set to consume agricultural waste or naturally ignited in forests or peatlands, open-burning fires impact the global climate system in two ways which, to some extent, cancel each other out. On one hand, they generate a significant fraction of the world’s carbon dioxide emissions, which drive up the average global surface temperature. On the other hand, they produce atmospheric aerosols, organic carbon, black carbon, and sulfate-bearing particulates that can lower that temperature either directly, by reflecting sunlight skyward, or indirectly, by increasing the reflectivity of clouds. Because wildfire aerosols play a key role in determining the future of the planet’s temperature and precipitation patterns, it’s crucial that today’s climate models — upon which energy and climate policymaking depend — accurately represent their impact on the climate system.
>> Read the Full Article

Wildlife ecologists who study the effects of climate change assume, with support from several studies, that warming temperatures caused by climate change are forcing animals to move either northward or upslope on mountainsides to stay within their natural climate conditions.
But a new study of lowland and higher-mountain bird species by wildlife ecologists Bill DeLuca and David King at the University of Massachusetts Amherst now reports an unexpected and “unprecedented” inconsistency in such shifts. The majority of the mountain bird community responded against expectation and shifted downslope despite warming trends in the mountains. They say the result “highlights the need for caution when applying conventional expectations to species’ responses to climate change.”
>> Read the Full Article
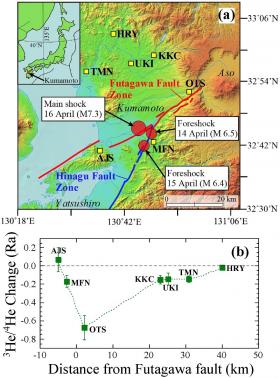
Researchers at the University of Tokyo and their collaborators have revealed a relationship between helium levels in groundwater and the amount of stress exerted on inner rock layers of the earth, found at locations near the epicenter of the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake. Scientists hope the finding will lead to the development of a monitoring system that catches stress changes that could foreshadow a big earthquake.
Several studies, including some on the massive earthquake in Kobe, Japan, in 1995, have indicated that changes to the chemical makeup of groundwater may occur prior to earthquakes. However, researchers still needed to accumulate evidence to link the occurrence of earthquakes to such chemical changes before establishing a strong correlation between the two.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment