
Faced with a lawsuit by 15 states, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency announced this week it would no longer delay the implementation of a rule requiring states to reduce emissions of smog-creating air pollution.
Crafted by the Obama administration in 2015, the regulation calls for states to begin meeting stricter ozone standards as of October 1, 2017, lowering the air pollution limit from 0.075 parts per million to 0.070 ppm. Ground-level ozone, or smog, is created when pollutants from cars, power plants, and other common industrial activities react with sunlight. It can cause respiratory and other health problems. In June, U.S. EPA head Scott Pruitt announced the agency would delay implementation of the new standards by one year.
>> Read the Full Article
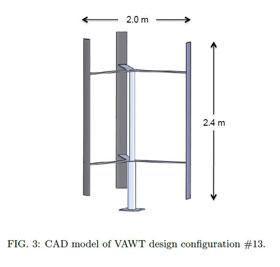
According to a prediction made by the U.S. Department of Energy, wind energy could provide 20 percent of electricity in the U.S. by the year 2030. This has motivated researchers from the University of Utah’s Department of Mechanical Engineering to investigate the performance capabilities and financial benefits of vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) in urban and suburban areas.
A VAWT is a wind turbine design where the generator is vertically oriented in the tower, rather than sitting horizontally on top. While there are many VAWT designs, the one used in this study is called the straight-blade Darrieus type or H-rotor turbine.
According to the researchers, small VAWTs possess the ability to effectively operate in the presence of high turbulent flow, which makes them ideal energy harvesting devices in urban and suburban environments. In an article in this week’s Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, from AIP Publishing, the authors present results indicating that an optimally designed VAWT system can financially compete with fossil-fuel based power plants in urban and suburban areas, and even spearhead the development of a net-zero energy building or city.
>> Read the Full Article
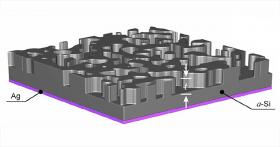
Design and nanomanufacturing have collided inside of a Northwestern University laboratory.
An interdisciplinary team of researchers has used mathematics and machine learning to design an optimal material for light management in solar cells, then fabricated the nanostructured surfaces simultaneously with a new nanomanufacturing technique.
>> Read the Full Article
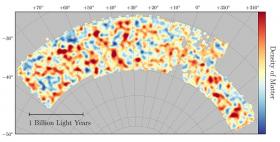
Astrophysicists have a fairly accurate understanding of how the universe ages: That’s the conclusion of new results from the Dark Energy Survey (DES), a large international science collaboration, including researchers from the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, that put models of cosmic structure formation and evolution to the most precise test yet.
The survey’s researchers analyzed light from 26 million galaxies to study how structures in the universe have changed over the past 7 billion years – half the age of the universe. The data were taken with the DECam, a 570-megapixel camera attached to the 4-meter Victor M. Blanco Telescope at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in Chile.
>> Read the Full Article

A pioneering new study is set to help surgeons repair hearts without damaging precious tissue.
A team of scientists from Liverpool John Moores University (LJMU), The University of Manchester, Aarhus University and Newcastle University, have developed a way of producing 3D data to show the cardiac conduction system - the special cells that enable our hearts to beat – in unprecedented detail. The findings were published in Scientific Reports.
>> Read the Full Article

Astronomers like to say we are the byproducts of stars, stellar furnaces that long ago fused hydrogen and helium into the elements needed for life through the process of stellar nucleosynthesis.
As the late Carl Sagan once put it: “The nitrogen in our DNA, the calcium in our teeth, the iron in our blood, the carbon in our apple pies were made in the interiors of collapsing stars. We are made of star stuff.”
But what about the heavier elements in the periodic chart, elements such as gold, platinum and uranium?
>> Read the Full Article
Since causing major outbreaks in Saudi Arabia in 2014, and in Korea a year later, the virus that causes Middle East Respiratory Syndrome is laying low. But by no means has it disappeared: A recent cluster of 34 cases cropped up in July in Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia’s capital. The dromedary camels who harbored the virus for more than 20 years aren’t going anywhere, and neither is MERS.
>> Read the Full Article

On the North Slope of Alaska, snow is melting earlier in the spring and the snow-in date is happening later in the fall, according to a new study by CIRES and NOAA researchers. Atmospheric dynamics and sea ice conditions are behind this lengthening of the snow-free season, the scientists found, and the consequences are far reaching—including birds laying eggs sooner and iced-over rivers flowing earlier.
“The timing of snowmelt and length of the snow-free season significantly impacts weather, the permafrost, and wildlife—in short, the Arctic terrestrial system as a whole,” said Christopher Cox, a scientist with CIRES at the University of Colorado Boulder and NOAA’s Physical Sciences Division in Boulder, Colorado. The study has been accepted for publication in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society.
>> Read the Full Article

Using isotope fingerprints in feathers, researchers have pinpointed the northern breeding grounds of a small, colourful songbird.
Myrtle warblers breed across much of Canada and the eastern United States, but winter in two distinct groups—one along the Atlantic and Gulf coasts, another along the US Pacific Coast. They are also one of the few breeds of eastern warbler that have been able to extend their range into the far northwest of the continent.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment