
It looks like a real heart. And this is the goal of the first entirely soft artificial heart: to mimic its natural model as closely as possible. The silicone heart has been developed by Nicholas Cohrs, a doctoral student in the group led by Wendelin Stark, Professor of Functional Materials Engineering at ETH Zurich. The reasoning why nature should be used as a model is clear. Currently used blood pumps have many disadvantages: their mechanical parts are susceptible to complications while the patient lacks a physiological pulse, which is assumed to have some consequences for the patient.
>> Read the Full Article

Over the next four months, NOAA scientists will launch unmanned ocean vehicles, called Saildrones, from the Arctic to the tropical Pacific Ocean to help better understand how changes in the ocean are affecting weather, climate, fisheries and marine mammals. The wind and solar-powered research vehicles that resemble a sailboat will travel thousands of miles across the ocean, reaching some areas never before surveyed with such specialized technology.
>> Read the Full Article

NOAA’s Annual Greenhouse Gas Index, which tracks the warming influence of long-lived greenhouse gases, has increased by 40 percent from 1990 to 2016 -- with most of that attributable to rising carbon dioxide levels, according to NOAA climate scientists.
The role of greenhouse gases on influencing global temperatures is well understood by scientists, but it’s a complicated topic that can be difficult to communicate. In 2006, NOAA scientists introduced the Annual Greenhouse Gas Index as a way to help policymakers, educators and the public understand changes in the direct climate warming influence exerted by greenhouse gas levels over time.
>> Read the Full Article

Drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have been around since the early 1900s. Originally used for military operations, they became more widely used after about 2010 when electronic technology got smaller, cheaper and more efficient, prices on cameras and sensors dropped, and battery power improved. Where once scientists could only observe earth from above by using manned aircraft or satellites, today they are expanding, developing and refining their research thanks to drones.
>> Read the Full Article

Rising temperatures due to global warming will make it harder for many aircraft around the world to take off in coming decades, says a new study. During the hottest parts of the day, 10 to 30 percent of fully loaded planes may have to remove some fuel, cargo or passengers, or else wait for cooler hours to fly, the study concludes. The study, which is the first such global analysis, appears today in the journal Climatic Change.
>> Read the Full Article

Struvite may not be a household word, but it is all too familiar to the operators of wastewater treatment plants.
A crystalline mineral known chemically as magnesium ammonium phosphate hexahydrate, struvite occurs naturally in decomposing organic materials such as sludge from animal wastes and from treated wastewater.
>> Read the Full Article

The effects of neonicotinoid insecticides on bees has been widely covered in the news recently, with laboratory-based studies suggesting that the chemicals are harmful, and field studies which are much less clear cut. Adding to current knowledge on the topic, new research published in the Journal of Apicultural Research further explores the effects that these chemicals may have on social behavior and learning in honey bees.
>> Read the Full Article
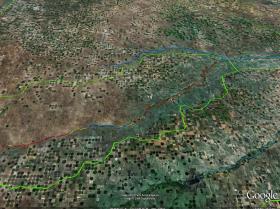
Farmers in the Great Plains of Nebraska, Colorado, Kansas and the panhandle of Texas produce about one-sixth of the world’s grain, and water for these crops comes from the High Plains Aquifer — often known as the Ogallala Aquifer — the single greatest source of groundwater in North America. A team of researchers, including Colorado State University Professor Kurt Fausch and Jeff Falke, a CSU alumnus and an assistant professor at the University of Alaska Fairbanks, have discovered that more than half a century of groundwater pumping from the aquifer has led to long segments of rivers drying up and the collapse of large-stream fishes.
>> Read the Full Article

Salt can be good, and it can also be bad. Sprinkled on food, it makes things tastier, but it may also raise your blood pressure. Spread on winter roads, it can make driving safer, but the melting runoff contaminates nearby lakes and ponds.
In a study that gathered data from hundreds of lakes in the Northeast and the Midwest, a Dartmouth researcher and colleagues have found dramatic evidence of highway salt’s impact.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment