
Prairie dogs in the wild are less likely to succumb to plague after they ingest peanut-butter-flavored bait that contains a vaccine against the disease, according to a U.S. Geological Survey study published today in the journal EcoHealth.
In an effort to increase populations of endangered black-footed ferrets and conserve the prairie dogs they rely on for survival, it is essential for land managers to control outbreaks of the bacterial disease also known as sylvatic plague. The plague affects numerous wild animal species, and domestic animals and humans are susceptible as well.
>> Read the Full Article

Coastal communities are struggling with the complex social and ecological impacts of a growing global hunger for a seafood delicacy, according to a new study from the University of British Columbia.
“Soaring demand has spurred sea cucumber booms across the globe,” says lead author Maery Kaplan-Hallam, who conducted the research as a master’s student with the Institute for Resources, Environment and Sustainability (IRES) at UBC.
>> Read the Full Article
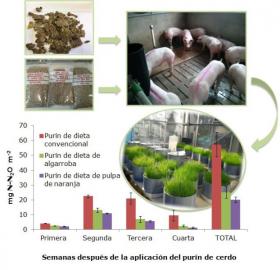
A research of UPM and UPV has shown that the inclusion of agroindustrial by-products in pig feed can reduce the nitrous oxide emissions (N2O) of the slurry used as manures up to 65%.
The aim of this study carried out by UPM researchers with the collaboration of Institute for Animal Science and Technology of UPV was to influence the ingredients of pig diet to modify the composition of slurry used as manures and to assess the possible variations on N2O emissions.
>> Read the Full Article
A team of scientists led by the Universities of Leicester and East Anglia are leading research to protect wildlife by using satellite data to identify monkey populations that have declined through hunting.
In a new article in the journal Nature Ecology and Evolution, a working group chaired by Professor Heiko Balzter, from the National Centre for Earth Observation at the University of Leicester, has looked at ways in which an array of technologies could be used to identify how many species are alive in an area and the risks they may be exposed to.
>> Read the Full Article
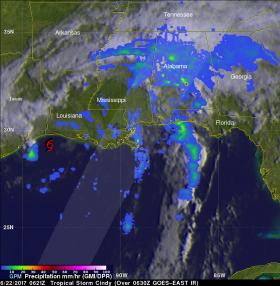
NASA's Aqua satellite analyzed Tropical Storm Cindy in infrared light to identify areas of strongest storms and the Global Precipitation Measurement mission or GPM satellite found locations of heaviest rainfall as Cindy was making landfall along the U.S. Gulf Coast states.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite looked at Tropical Depression Cindy in infrared light. The AIRS image was taken on June 21 at 19:53 UTC (3:53 p.m. EST) and showed some cloud top temperatures of thunderstorms near the center of circulation as cold as minus 63 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 53 degrees Celsius). NASA research has shown the storms with cloud tops that cold have the potential to generate heavy rainfall.
The infrared data was false-colored at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, where AIRS data is managed.
Cindy made landfall around 3 a.m. CDT in southwestern Louisiana. At that time, the National Hurricane Center or NHC said that Cindy was centered about 30 miles (45 km) west-southwest of Lake Charles, Louisiana.
>> Read the Full Article

Scientists have developed a new low-temperature catalyst for producing high-purity hydrogen gas while simultaneously using up carbon monoxide (CO). The discovery—described in a paper set to publish online in the journal Science on Thursday, June 22, 2017—could improve the performance of fuel cells that run on hydrogen fuel but can be poisoned by CO.
“This catalyst produces a purer form of hydrogen to feed into the fuel cell,” said José Rodriguez, a chemist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory. Rodriguez and colleagues in Brookhaven’s Chemistry Division—Ping Liu and Wenqian Xu—were among the team of scientists who helped to characterize the structural and mechanistic details of the catalyst, which was synthesized and tested by collaborators at Peking University in an effort led by Chemistry Professor Ding Ma.
>> Read the Full Article

When her kids were young, Tracey Woodruff, PhD, MPH, knew more than most people about environmental toxics. After all, she was a senior scientist at the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). But even she never dreamed, as she rocked her children to sleep at night, that the plastic baby bottles she used to feed them contained toxic chemicals that could leach into the warm milk.
Back then, in the late 1990s, it wasn’t widely known that the chemicals used in plastic sippy cups and baby bottles can potentially disrupt child development by interfering with the hormone system. That, in turn, could alter the functionality of their reproductive systems or increase their risk of disease later in their lives.
>> Read the Full Article

A team of chemists from the University of Kentucky and the Institute of Physics Research of Mar del Plata in Argentina has just reported a way to trigger a fundamental step in the mechanism of photosynthesis, providing a process with great potential for developing new technology to reduce carbon dioxide levels.
Led by Marcelo Guzman, an associate professor of chemistry in the UK College of Arts and Sciences, and Ruixin Zhou, a doctoral student working with Guzman, the researchers used a synthetic nanomaterial that combines the highly reducing power of cuprous oxide (Cu2O) with a coating of oxidizing titanium dioxide (TiO2) that prevents the loss of copper (I) ion in the catalyst. The catalyst made of Cu2O/TiO2 has the unique ability to transfer electrons for reducing the atmospheric greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) while simultaneously breaking the molecule of water (H2O). The unique feature of this catalyst for electron transfer mimics the so called “Z-scheme” mechanism from photosynthesis.
>> Read the Full Article

Almost 25 percent of the world’s malnourished population lives in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), where more than 300 million people depend on maize (corn) for much of their diet. The most widely-produced crop by harvested area in SSA, maize is also highly sensitive to drought. Because maize in this region is grown largely on rainfed rather than irrigated land, any future changes in precipitation patterns due to climate change could significantly impact crop yields. Assessing the likely magnitude and locations of such yield changes in the coming decades will be critical for decision makers seeking to help their nations and regions adapt to climate change and minimize threats to food security and to rural economies that are heavily dependent on agriculture.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment