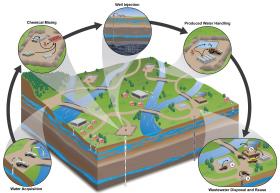
Wastewater from oil and gas operations – including fracking for shale gas – at a West Virginia site altered microbes downstream, according to a Rutgers-led study.
The study, published recently in Science of the Total Environment, showed that wastewater releases, including briny water that contained petroleum and other pollutants, altered the diversity, numbers and functions of microbes. The shifts in the microbial community indicated changes in their respiration and nutrient cycling, along with signs of stress.
>> Read the Full Article

If you asked Richard Sparling, what he did during his sabbatical early last year, he’d probably say “fishing in New Zealand.”
But this ambiguous answer by the department of microbiology associate professor does not tell the whole story.
>> Read the Full Article

Almost one year ago, borophene didn’t even exist. Now, just months after a Northwestern Engineering and Argonne National Laboratory team discovered the material, another team led by Mark Hersam is already making strides toward understanding its complicated chemistry and realizing its electronic potential.
>> Read the Full Article

NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope has revealed the first known system of seven Earth-size planets around a single star. Three of these planets are firmly located in the habitable zone, the area around the parent star where a rocky planet is most likely to have liquid water.
The discovery sets a new record for greatest number of habitable-zone planets found around a single star outside our solar system. All of these seven planets could have liquid water – key to life as we know it – under the right atmospheric conditions, but the chances are highest with the three in the habitable zone.
>> Read the Full Article

When deciding what crops to grow during a season, growers look at several factors. Do the crops have a good yield in their area? Does the area currently have the resources - usually water - to grow that crop? Will the crop give a return on the investment? And, what are the future effects that growing that crop might have on the grower’s fields?
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment