
E-cigarettes are often perceived to be less harmful than their traditional counterparts, but they could still expose the people who “vape” and those around them to harmful compounds. Researchers now report in ACS’ journal Environmental Science & Technology that heavy use and secondhand emissions could lead to inhaled levels of toxins that exceed set exposure limits. But under typical use, secondhand exposure would have a lower impact on health than second- and third-hand cigarette smoke.
>> Read the Full Article

Microbes mediate the global marine cycles of elements, modulating atmospheric carbon dioxide and helping to maintain the oxygen we all breathe, yet there is much about them scientists still don’t understand. Now, an award from the Simons Foundation will give researchers from MIT's Darwin Project access to bigger, better computing resources to model these communities and probe how they work.
The simulations of plankton populations made by Darwin Project researchers have become increasingly computationally demanding. MIT Professor Michael "Mick" Follows and Principal Research Engineer Christopher Hill, both affiliates of the Darwin Project, were therefore delighted to learn of their recent Simons Foundation award, providing them with enhanced compute infrastructure to help execute the simulations of ocean circulation, biogeochemical cycles, and microbial population dynamics that are the bread and butter of their research.
>> Read the Full Article

Production of liquid fuels from regenerative electric power is a major component of the energy turnaround. The first 200 l of synthetic fuel have now been produced from solar energy and the air’s carbon dioxide by Fischer-Tropsch synthesis under the SOLETAIR project. Here, INERATEC, a spinoff of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), cooperates with Finnish partners. The mobile chemical pilot plant that can be used decentrally produces gasoline, diesel, and kerosene from regenerative hydrogen and carbon dioxide. It is so compact that it fits into a shipping container.
>> Read the Full Article
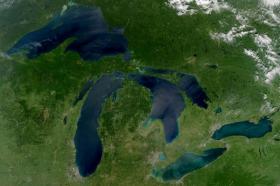
The Great Lakes could be in hot water if the quality of the research and partnerships are not improved, warns a University of Windsor professor.
“Fresh water is arguably the most important issue for the world going forward to support the planet,” said University of Windsor professor Aaron Fisk, the Tier 1 Canada Research Chair in Changing Great Lakes Ecosystems. “But the amount of resources that are dedicated to the Great Lakes from the U.S. and Canada is only a fraction of what is funded for the oceans.”
>> Read the Full Article

Simon Fraser University graduate student Oldooz Pooyanfar is monitoring what more than 20,000 honeybees housed in hives in a Cloverdale field are “saying” to each other—looking for clues about their health.
Pooyanfar’s technology is gleaning communication details from sound within the hives with her beehive monitoring system—technology she developed at SFU. She says improving knowledge about hone
>> Read the Full Article
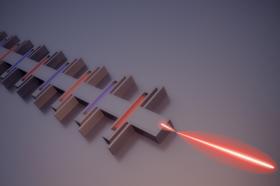
Terahertz radiation — the band of the electromagnetic spectrum between microwaves and visible light — has promising applications in medical and industrial imaging and chemical detection, among other uses.
But many of those applications depend on small, power-efficient sources of terahertz rays, and the standard method for producing them involves a bulky, power-hungry, tabletop device.
For more than 20 years, Qing Hu, a distinguished professor of electrical engineering and computer science at MIT, and his group have been working on sources of terahertz radiation that can be etched onto microchips. In the latest issue of Nature Photonics, members of Hu’s group and colleagues at Sandia National Laboratories and the University of Toronto describe a novel design that boosts the power output of chip-mounted terahertz lasers by 80 percent.
>> Read the Full Article

In a win-win for a cleaner planet, scientists have devised a way to use waste cooking oil and sulphur to extract the neurotoxin mercury from the environment.
For the first time, researchers have demonstrated that the dynamic new canola oil polymer can trap the most dangerous and common types of mercury pollution – mercury metal, mercury vapour and highly toxic organo-mercury compounds which harm both aquatic and terrestrial systems.
>> Read the Full Article

A new study by scientists at Portland State University and the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) at the University of Colorado Boulder has found that the effects of climate change, which are apparent in other parts of the Antarctic continent, are not yet observed for glaciers in the western Ross Sea coast.
Published online ahead of print for the journal Geology, the study found that the pattern of glacier advance and retreat has not changed along the western Ross Sea coast, in contrast to the rapidly shrinking glaciers on the Antarctic Peninsula.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment