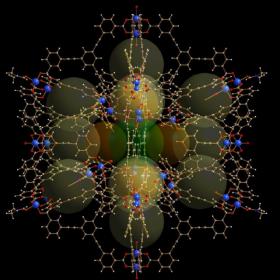
Scientists from Trinity College Dublin and AMBER, the Science Foundation Ireland-funded materials science research centre hosted in Trinity College Dublin, have created ‘molecular cages’ that can maximise the efficiency of converting molecules in chemical reactions, and that may in future also be used as sensors and drug-delivery agents. The cages can be packed with different molecules, many of which have a specific task or functionality.
>> Read the Full Article
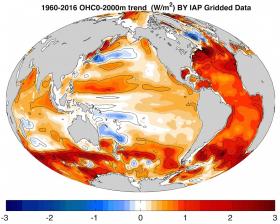
More than 90% of the earth’s energy imbalance (EEI) in the climate system is sequestered in the ocean and consequently the ocean heat content (OHC) is increasing. Therefore, OHC is one of the most important indicators of global warming. During the past 30 years, many independent groups worked to estimate historical OHC changes. However, large uncertainty has been found among the published global OHC time series. For example, during the current surge of research on the so-called “hiatus” or “slowdown”, different scientific studies draw quite different conclusions on the key scientific question such as “Where is the heat redistributed in the ocean?” This motivates us to give a detailed analysis about global and basin OHC changes based on multiple ocean datasets.
>> Read the Full Article

India and Pakistan are among the most heavily irrigated nations on earth, producing enough wheat, corn, and other crops to feed their combined populations of 1.5 billion. But in South Asia’s breadbasket, which includes the Punjab region, farmers have pumped water out of the ground so heedlessly for so long that scientists now estimate aquifers there could run dry by mid-century. Add to that the disruptive effects of climate change and it’s clear that South Asian agriculture is facing a perilous future.
>> Read the Full Article
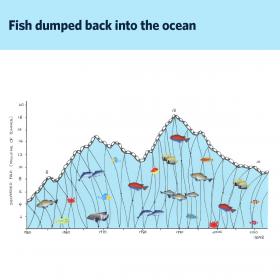
ndustrial fishing fleets dump nearly 10 million tonnes of good fish back into the ocean every year, according to new research.
The study by researchers with Sea Around Us, an initiative at the University of British Columbia’s Institute for the Oceans and Fisheries and the University of Western Australia, reveals that almost 10 per cent of the world’s total catch in the last decade was discarded due to poor fishing practices and inadequate management. This is equivalent to throwing back enough fish to fill about 4,500 Olympic sized swimming pools every year.
>> Read the Full Article

A Canadian technology that can identify a substance by scanning it — as a character in Star Trek might — could become a crucial tool to capture DNA data in the environment and protect it.
DNA barcoding, developed at the University of Guelph by Professor Paul Hebert, uses genetic variations to identify different species. It’s similar to how a supermarket checkout scanner reads variations in a UPC barcode’s lines to identify a product you buy.
>> Read the Full Article
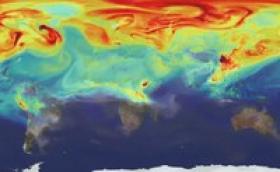
The world needs high-speed climate action for an immediate bending-down of the global greenhouse-gas emissions curve, leading experts caution. Aggressive reduction of fossil-fuel usage is the key to averting devastating heat extremes and unmanageable sea level rise, the authors argue in a comment published in the renowned scientific journal Nature this week. In the run-up to the G20 summit of the planet’s leading economies, the article sets six milestones for a clean industrial revolution. This call for strong short-term measures complements the longer-term 'carbon law' approach introduced earlier this year by some of the current co-authors, including the Potsdam Institute’s Director Hans Joachim Schellnhuber, in the equally eminent journal Science. Thus a full narrative of deep decarbonization emerges.
>> Read the Full Article
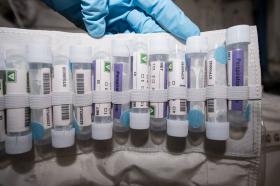
Wherever you find people, you also find bacteria and other microorganisms. The International Space Station is no exception.
That generally is not a problem. For one thing, the space station is kept cleaner than many environments on Earth. Routine cleaning activities are included on astronaut task schedules. Cargo sent to the station, and the vehicles that carry it, undergo a rigorous cleaning process and monitoring for microorganisms before launch. Crew members assigned to the space station spend 10 days in pre-flight quarantine.
For another, scientists regularly monitor the interior of this and other spacecraft, a process that started with the Apollo missions.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment