
While climate scientists agree that human-caused climate change is influencing weather, they have often been hesitant to draw direct linkages between this phenomenon and specific extreme weather events. The reason? When studying a particular event such as a superstorm or severe heatwave, it can be challenging to tease apart human influence from the natural variability of the weather. But that’s changing.
In a new study, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Stanford professor of Earth system science Noah Diffenbaugh and a team of colleagues outline a four-step framework for testing whether global warming has contributed to particular weather events. The collaborative effort involves researchers from several universities including Northwestern and is the latest in the growing field of “event attribution analysis,” which combines statistical analyses of climate observations with increasingly powerful computer models to study the influence of climate change on individual extreme weather events.
>> Read the Full Article
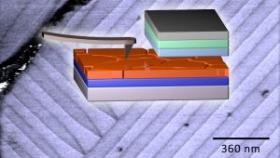
Solar cells based on perovskites reach high efficiencies: They convert more than 20 percent of the incident light directly into usable power. On their search for underlying physical mechanisms, researchers of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have now detected strips of nanostructures with alternating directions of polarization in the perovskite layers. These structures might serve as transport paths for charge carriers. This is reported in the Energy & Environmental Science Journal.
The perovskites used by the KIT scientists are metal organic compounds with a special crystal structure and excellent photovoltaic properties. Since their discovery in 2009, perovskite solar cells have experienced a rapid development. Meanwhile, they reach power conversion efficiencies of more than 20 percent. This makes them one of the most promising photovoltaic technologies. Research into perovskite solar cells, however, faces two special challenges: The light-absorbing layers have to be made more robust to environmental impacts and the lead contained therein has to be replaced by environmentally more compatible elements. This requires in-depth understanding of physical mechanisms that enable the high conversion rate of absorbed solar energy into electric power.
>> Read the Full Article

While recent media reports have condemned a commonly used agricultural pesticide as detrimental to honey bee health, scientists with the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture have found that the overall health of honey bee hives actually improves in the presence of agricultural production.
The study, “Agricultural Landscape and Pesticide Effects on Honey Bee Biological Traits,” which was published in a recent issue of the Journal of Economic Entomology, evaluated the impacts of row-crop agriculture, including the traditional use of pesticides, on honey bee health. Results indicated that hive health was positively correlated to the presence of agriculture. According to the study, colonies in a non-agricultural area struggled to find adequate food resources and produced fewer offspring.
>> Read the Full Article

In May, a team of Goddard scientists will begin measuring greenhouse gases over the Mid-Atlantic region — an area chosen in part because it encompasses a range of vegetation, climate, and soil types that would influence the exchange of carbon dioxide and methane between the Earth and the atmosphere.
The airborne campaign, called the Carbon Airborne Flux Experiment, or CARAFE, could help scientists better understand the exchange process, also known as flux, and improve computer models that predict Earth’s carbon sinks, natural or artificial areas that absorb carbon dioxide or methane.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment