A powerful new material developed by Northwestern University chemist William Dichtel and his research team could one day speed up the charging process of electric cars and help increase their driving range.
An electric car currently relies on a complex interplay of both batteries and supercapacitors to provide the energy it needs to go places, but that could change.
"Our material combines the best of both worlds -- the ability to store large amounts of electrical energy or charge, like a battery, and the ability to charge and discharge rapidly, like a supercapacitor," said Dichtel, a pioneer in the young research field of covalent organic frameworks (COFs).
A powerful new material developed by Northwestern University chemist William Dichtel and his research team could one day speed up the charging process of electric cars and help increase their driving range.
An electric car currently relies on a complex interplay of both batteries and supercapacitors to provide the energy it needs to go places, but that could change.
"Our material combines the best of both worlds -- the ability to store large amounts of electrical energy or charge, like a battery, and the ability to charge and discharge rapidly, like a supercapacitor," said Dichtel, a pioneer in the young research field of covalent organic frameworks (COFs).
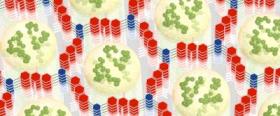
Dichtel and his research team have combined a COF -- a strong, stiff polymer with an abundance of tiny pores suitable for storing energy -- with a very conductive material to create the first modified redox-active COF that closes the gap with other older porous carbon-based electrodes.
"COFs are beautiful structures with a lot of promise, but their conductivity is limited," Dichtel said. "That's the problem we are addressing here. By modifying them -- by adding the attribute they lack -- we can start to use COFs in a practical way."
Continue reading at EurekAlert!
Image: A conductive polymer (green) formed inside the small holes of a hexagonal framework (red and blue) work together to store electrical energy rapidly and efficiently.
Credit: William Dichtel, Northwestern University