Sulfur dioxide is an air pollutant that causes acid rain, haze and many health-related problems. It is produced predominantly when coal is burned to generate electricity.
Sulfur dioxide is an air pollutant that causes acid rain, haze and many health-related problems. It is produced predominantly when coal is burned to generate electricity.
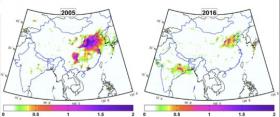
Although China and India remain the world’s largest consumers of coal, a new University of Maryland-led study found that China’s sulfur dioxide emissions fell by 75 percent since 2007, while India’s emissions increased by 50 percent. The results suggest that India is becoming, if it is not already, the world’s top sulfur dioxide emitter.
“The rapid decrease of sulfur dioxide emissions in China far exceeds expectations and projections,” said Can Li, an associate research scientist in UMD’s Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Centerand first author on the study. “This suggests that China is implementing sulfur dioxide controls beyond what climate modelers have taken into account.”
The study was published in the journal Scientific Reports on November 9, 2017.
Read more at University of Maryland
Image: Two maps compare total annual sulfur dioxide amounts for India and China during 2005 (left) and 2016 based on Ozone Monitoring Instrument measurements. Purple depicts the highest concentrations while white depicts the lowest. Note the decrease in size of the purple region over northeastern China. (Credit: Chris McLinden, Environment and Climate Change Canada)