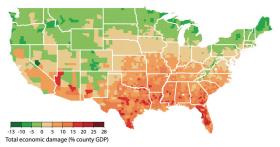
Climate scientists agree that this century is getting much warmer and that such warming will likely bring economic pain to the U.S., but economists aren't sure how much. Now, a team of scientists and economists, writing in the upcoming issue of the journal Science, says it can at least tell which parts of the country are likely to suffer the most.
>> Read the Full Article

The world’s open grasslands and the beneficial fires that sustain them have shrunk rapidly over the past two decades, thanks to a massive increase in agriculture, according to a new study led by University of California, Irvine and NASA researchers published today in Science.
Analyzing 1998 to 2015 data from NASA’s Terra and Aqua satellites, the international team found that the total area of Earth’s surface torched by flames had fallen by nearly 25 percent, or 452,000 square miles (1.2 million square kilometers). Decreases were greatest in Central America and South America, across the Eurasian steppe and in northern Africa, home to fast-disappearing lions, rhinoceroses and other iconic species that live on these fire-forged savannas.
>> Read the Full Article
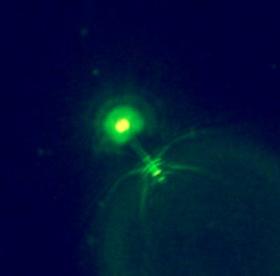
A group of scientists from several research centres and international universities led by Manuel Martínez García, from the University of Alicante Research Group in Molecular Microbian Ecology has discovered forty-four of the most abundant new viruses in all the Earth's oceans. The finding has been achieved thanks to the application of cutting-edge techniques that mix flow cytometry and genomics and molecular biology techniques. The findings will appear today, 23 June 2017, in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
>> Read the Full Article
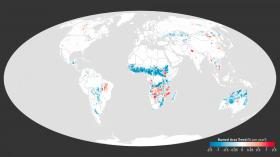
Shifting livelihoods across the tropical forest frontiers of South America, the Eurasian Steppe, and the savannas of Africa are altering landscapes and leading to a significant decline in the amount of land burned by fire each year, a trend that NASA satellites have detected from space.
The ongoing transition from nomadic cultures to settled lifestyles and intensifying agriculture has led to a steep drop not only in the use of fire on local lands, but in the prevalence of fire worldwide, researchers at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and colleagues found.
>> Read the Full Article

A new study of 60 million Americans—about 97% of people age 65 and older in the United States—shows that long-term exposure to airborne fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and ozone increases the risk of premature death, even when that exposure is at levels below the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) currently established by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health researchers found that men, blacks, and low-income populations had higher risk estimates from PM2.5 exposure compared with the national average, with blacks having mortality risks three times higher than the national average.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment