
Researchers at the University of Waterloo have developed a system for service vehicles that could reduce emissions and save companies and governments millions of dollars per year in fuel costs.
In a study recently published in Energy, Waterloo engineers found a way to capture waste energy from service vehicles, such as buses or refrigerated food delivery trucks, as they are slowing down.
They also figured out how to use that energy to replace the fossil fuels that are currently needed to operate secondary systems, such as air conditioning or refrigeration units, when the vehicles are stopped and idling.
>> Read the Full Article

Scientists at the University of Notre Dame have found that exposure to just 10 minutes of light at night suppresses biting and manipulates flight behavior in the Anopheles gambiae mosquito, the major vector for transmission of malaria in Africa, according to new research published in the journal Parasites and Vectors.
Critical behaviors exhibited by the species, such as feeding, egg laying and flying, are time-of-day specific, including a greater propensity for nighttime biting. A recent report from the World Health Organization stated an estimated 212 million people worldwide are infected with the disease, resulting in 429,000 deaths – mostly children.
>> Read the Full Article
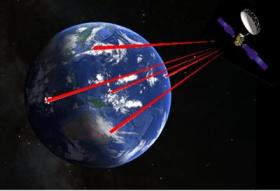
In a new study, researchers demonstrate ground-based measurements of quantum states sent by a laser aboard a satellite 38,000 kilometers above Earth. This is the first time that quantum states have been measured so carefully from so far away.
“We were quite surprised by how well the quantum states survived traveling through the atmospheric turbulence to a ground station,” said Christoph Marquardt from the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light, Germany. “The paper demonstrates that technology on satellites, already space-proof against severe environmental tests, can be used to achieve quantum-limited measurements, thus making a satellite quantum communication network possible. This greatly cuts down on development time, meaning it could be possible to have such a system as soon as five years from now.”
>> Read the Full Article

Fish is a healthy diet, it supplies important omega-3 fatty acids and trace elements like iodine and selenium. However, eating fish caught in certain regions can sometimes also have its risks. In Bavaria, there have recently been reports of multiple cases of diarrhoea, vomiting and cold pain following consumption of imported deep-frozen fish. The symptoms are typical signs of ciguatera - one of the most frequent fish poisonings worldwide caused by ciguatoxins in edible fish.
>> Read the Full Article

The Cape Cod Canal is a serpentine artificial waterway that winds eight miles from Cape Cod Bay to Buzzards Bay. On warm summer evenings, anglers jostle along its banks casting for striped bass. That’s what 29-year-old Justin Sprague was doing the evening of August 6, 2013, when he caught a fish from the future.
At first, Sprague thought the enormous fish that engulfed his Storm blue herring lure was a shark. But as he battled the behemoth in the gloaming — the fish leaping repeatedly, crashing down in sheets of spray — he realized he’d hooked something far weirder. When the fisherman finally dragged his adversary onto the beach, a small crowd gathered to admire the creature’s metallic body, flared dorsal fin, and rapier-like bill. Sprague had caught a sailfish.
>> Read the Full Article
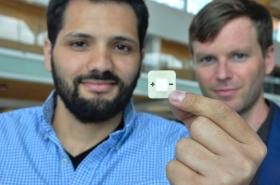
Simon Fraser University researchers are developing a tiny power source that activates with only a few drops of water and can provide instant power up to 100 minutes before being tossed away.
The patent-pending biodegradable PowerPAD (Power: Portable And Disposable) is a single-use disposable battery—a mere inch in diameter—in which water stimulates a chemical reaction that changes the oxidization of its atoms.
>> Read the Full Article

After much of Cape Breton’s oyster sector closed in 2002, Dr. Sarah Stewart-Clark, an assistant professor in the Department of Animal Science and Aquaculture in Dal’s Faculty of Agriculture, was determined to find a way to rebuild this 100-year-old economic and cultural activity.
The sector’s closure was the result of a pathogen found in oysters located in the Bras D’Ors Lakes. Known as the Haplosporidium nelsonii parasite (MSX), the disease causes high mortality in oyster populations but has no impact on humans.
>> Read the Full Article

Large-scale interventions to water resources, such as irrigation, dams and reservoirs, and water withdrawals, have been essential to human development. But interventions tend to solve water scarcity problems at a local level, while aggravating water scarcity downstream. In a new study published in the journal Nature Communications, researchers have now assessed the impacts of human interventions on water scarcity at a global scale.
>> Read the Full Article

The long range of airborne drones helps them perform critical tasks in the skies. Now MIT spinout Open Water Power (OWP) aims to greatly improve the range of unpiloted underwater vehicles (UUVs), helping them better perform in a range of applications under the sea.
Recently acquired by major tech firm L3 Technologies, OWP has developed a novel aluminum-water power system that’s safer and more durable, and that gives UUVs a tenfold increase in range over traditional lithium-ion batteries used for the same applications.
>> Read the Full Article

Find related stories on NSF's geosciences risk and resilience interest area.
Understanding "slow-slip" earthquakes on the seafloor -- seismic events that occur over a period of days or weeks -- is giving researchers new insights into undersea earthquakes and the subsequent creation of tsunamis. Through an ocean discovery program supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF), scientists are studying the seafloor off the coast of Japan. The region could provide vital clues.
Two tectonic plates, the Pacific Plate and the Eurasian Plate, meet there. In this ocean trench zone, the Pacific plate slides beneath the Eurasian plate. Such subduction zones are often associated with large earthquakes.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment