
If you think self-driving cars can’t get here soon enough, you’re not alone. But programming computers to recognize objects is very technically challenging, especially since scientists don’t fully understand how our own brains do it.
Now, Salk Institute researchers have analyzed how neurons in a critical part of the brain, called V2, respond to natural scenes, providing a better understanding of vision processing. The work is described in Nature Communications on June 8, 2017.
“Understanding how the brain recognizes visual objects is important not only for the sake of vision, but also because it provides a window on how the brain works in general,” says Tatyana Sharpee, an associate professor in Salk’s Computational Neurobiology Laboratory and senior author of the paper. “Much of our brain is composed of a repeated computational unit, called a cortical column. In vision especially we can control inputs to the brain with exquisite precision, which makes it possible to quantitatively analyze how signals are transformed in the brain.”
>> Read the Full Article
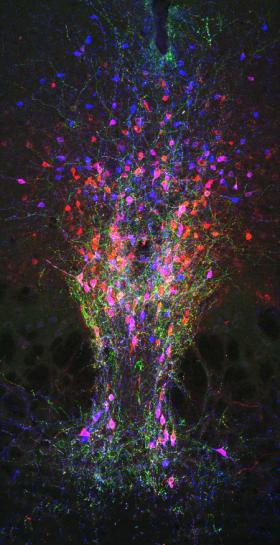
Caltech researchers have identified a neural circuit in the brain that controls wakefulness. The findings have implications for treating insomnia, oversleeping, and sleep disturbances that accompany other neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression.
The work was done in the laboratory of Viviana Gradinaru (BS '05), assistant professor of biology and biological engineering, Heritage Medical Research Institute Investigator, and director of the Center for Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience of the Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute for Neuroscience at Caltech. It appears in the June 8 online edition of the journal Neuron.
>> Read the Full Article

In the event of a natural disaster that disrupts phone and Internet systems over a wide area, autonomous aircraft could potentially hover over affected regions, carrying communications payloads that provide temporary telecommunications coverage to those in need.
However, such unpiloted aerial vehicles, or UAVs, are often expensive to operate, and can only remain in the air for a day or two, as is the case with most autonomous surveillance aircraft operated by the U.S. Air Force. Providing adequate and persistent coverage would require a relay of multiple aircraft, landing and refueling around the clock, with operational costs of thousands of dollars per hour, per vehicle.
>> Read the Full Article
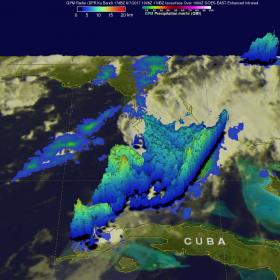
Extremely heavy rain has recently fallen over Florida and the Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM mission core satellite looked at that some of that rainfall on June 7. Rainfall records were broken on that date as the GPM satellite passed overhead from space.
Over 19 inches (482 mm) of rain had fallen in southeastern Florida during the past seven days beginning June 1. Record rainfall has been reported in Fort Lauderdale and West Palm. This extreme rainfall has led to flooding and flight cancellations.
>> Read the Full Article

The Sydney Harbour is renowned as a beautiful landmark straddling our thriving city but a new study has shown it is also a source of significant carbon emissions, which requires careful management as the city is poised to double its population by the end of the century.
That is the message of new research that has quantified CO2 emissions from the Harbour for the first time – found to be 1000 tonnes annually – equivalent to the pollution from about 200 cars.
>> Read the Full Article

Studying the food poisoning bacteria E. coli may have led scientists to discover a new and improved tool to detect cancer.
In a collaborative research project, scientists from Griffith University’s Institute for Glycomics, the University of Adelaide and University of Queensland have detailed their findings in a new paper published in Scientific Reports.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment