
This week the UK Government published its long awaited industrial strategy, marking a distinctive break from the previous Conservative regime. Gone is David Cameron's more laissez faire attitude to managing the economy. In its place is a more proactive approach, which seeks to stimulate industry with targeted investment. Taking advantage of the greater flexibility afforded by freedom from the EU's state aid rules the plan sees some exciting developments in the decarbonisation of the UK economy.
>> Read the Full Article

The co-authors from the Russian side are Oleg Gusev (Extreme Biology Lab, Kazan Federal University) and Vladimir Sychyov (Institute of Medical and Biological Problems of RAS).
As is well-known, space flights bring with them a unique set of health hazards. That includes bone and muscle deterioration. Loss of bone density is currently one of the most serious problems for astronauts. It is similar in nature to osteoporosis, an ailment common for senior people. Understanding microgravity and its effects on living organisms can help find new clinical methods of coping with this issue.
>> Read the Full Article
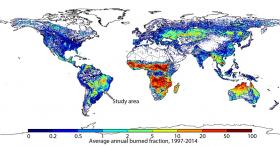
Pollution from the controlled fires that burn across Brazil's São Paulo state during the sugarcane-harvesting season has a negative impact on infant health nearby. But the health of those same infants likely benefits from the economic opportunities the fires bring to their parents.
Researchers at Princeton and Duke universities gathered information from satellites, pollution monitors and birth records to untangle those competing influences and accurately measure the impact of pollution from the fires. They found that exposure to pollution from the fires in the last few months of gestation leads to earlier birth and smaller babies, and they found some evidence of increased fetal mortality. Conditions in early life, including in utero, have been shown to affect children's long-term outcomes, not only in terms of health but also their educational and economic success.
>> Read the Full Article

Floating wetlands may seem odd but are perfectly natural. They occur when mats of vegetation break free from the shore of a body of water. That got ecological engineers curious about how they affect the water they bob up and down in.
A group from Saint Francis University in Pennsylvania and the University of Oklahoma, including researcher William Strosnider, has found that the floating wetlands show promise for water treatment. They engineered four different floating treatment wetlands designs using different materials and wetland plants.
>> Read the Full Article

Changes in rainfall and temperature are predicted to transform wetlands in the Gulf of Mexico and around the world within the century, a new study from the USGS and the University of Texas Rio Grande Valley concludes.
Sea-level rise isn’t the only aspect of climate change expected to affect coastal wetlands: changes in rainfall and temperature are predicted to transform wetlands in the Gulf of Mexico and around the world within the century. These changes will take place regardless of sea-level rise, a new study from the US Geological Survey and the University of Texas Rio Grande Valley concludes.
>> Read the Full Article

In the cold depths along the sea floor, Antarctic Bottom Waters are part of a global circulatory system, supplying oxygen-, carbon- and nutrient-rich waters to the world’s oceans. Over the last decade, scientists have been monitoring changes in these waters. But a new study from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) suggests these changes are themselves shifting in unexpected ways, with potentially significant consequences for the ocean and climate.
In a paper published January 25 in Science Advances, a team led by WHOI oceanographers Viviane Menezes and Alison Macdonald report that Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW) has freshened at a surprising rate between 2007 and 2016—a shift that could alter ocean circulation and ultimately contribute to rising sea levels.
>> Read the Full Article

COLUMBIA, Mo. – Polyhedral boranes, or clusters of boron atoms bound to hydrogen atoms, are transforming the biomedical industry. These manmade materials have become the basis for the creation of cancer therapies, enhanced drug delivery and new contrast agents needed for radioimaging and diagnosis. Now, a researcher at the University of Missouri has discovered an entirely new class of materials based on boranes that might have widespread potential applications, including improved diagnostic tools for cancer and other diseases as well as low-cost solar energy cells.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment