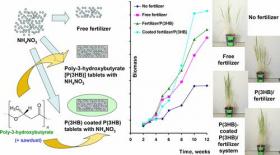
According to the head of the works Tatiana Volova, Professor of SibFU and the Head of Laboratory in the Institute of Biophysics KSC of SB RAS, development of a new generation of drugs with the use of bio-decomposable materials which decompose under the influence of the microflora to innocuous products and provide a gradual release of the active principle into the soil, is the newest area of research in the field of agriculture. For example, nitrogen is one of the elements, which is often lacking for the growth and development of plants. Plant-available nitrogen in the soil is usually small. Moreover, its compounds are chemically very mobile and easily leached from the soil. In this connection there is the task of developing such forms of nitrogen fertilizers that provide slow release nitrogen and the constancy of its concentration in the soil.
>> Read the Full Article
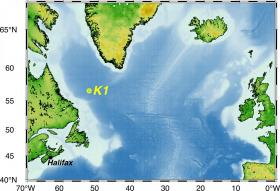
The Labrador Sea in the North Atlantic is one of the few areas in the world ocean where cold, saline seawater sinks to large depths and forms deep water. This convection process also transports oxygen into the deep sea. A team of scientists from Scripps Institution of Oceanography (San Diego, California), Dalhousie University (Halifax, Canada) and GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel have now published the analysis of data obtained from the mooring K1 in the international scientific journal Geophysical Research Letters. The results show that in winter 2014/2015 an unusually high amount of oxygen was absorbed by the ocean in the region. The actual oxygen uptake at the sea surface is very difficult to determine directly, but the scientists were able to derive the oxygen uptake from the oxygen content measured throughout the water column. One of the questions the scientists were concerned with: Can the strong oxygen uptake in the Labrador Sea compensate the global oxygen loss of the ocean?
>> Read the Full Article

Researchers from the United States and China have proposed an idea that could improve China’s air quality, but they’re not atmospheric scientists. They’re agronomists.
“China’s poor air quality is caused by a combination of coal burning and particulates from soil erosion. The Loess Plateau is the major source of erosion in China, and air quality there is just terrible. If erosion in the Loess Plateau can be improved, air quality will improve,” says D.K. Lee, an agronomist in the Department of Crop Sciences at the University of Illinois.
>> Read the Full Article
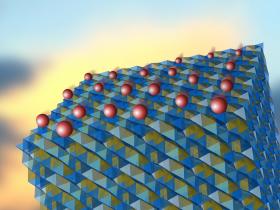
The modern world relies on portable electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, cameras or camcorders. Many of these devices are powered by lithium-ion batteries, which could be smaller, lighter, safer and more efficient if the liquid electrolytes they contain were replaced by solids. A promising candidate for a solid-state electrolyte is a new class of materials based on lithium compounds, presented by physicists from Switzerland and Poland.
>> Read the Full Article

In June 2017, three critically endangered North Atlantic right whale carcasses were spotted floating in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. In the weeks that followed the number of dead right whales rose to 10, while three more were found entangled alive in fishing gear. (The total number of deaths may be as high as 12.)
For a species with approximately 500 surviving animals in the world, this was a crisis — an unprecedented die-off signalling a troubled outlook for the species.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment