
Crop producers and scientists hold deeply different views on climate change and its possible causes, a study by Purdue and Iowa State universities shows. Associate professor of natural resource social science Linda Prokopy and fellow researchers surveyed 6,795 people in the agricultural sector in 2011-2012 to determine their beliefs about climate change and whether variation in the climate is triggered by human activities, natural causes or an equal combination of both.
>> Read the Full Article

The Southern Ocean plays an important role in the exchange of carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and the ocean. One aspect of this is the growth of phytoplankton, which acts as a natural sponge for carbon dioxide, drawing the troublesome greenhouse gas from the atmosphere into the sea. When these plankton die they can sink to the bottom of the ocean and store some of the carbon dioxide they have absorbed, a process scientists call the "biological carbon pump."
Although many areas of the Southern Ocean are rich in nutrients, they often lack iron, which limits phytoplankton growth. An important idea in oceanography is that adding iron to the Southern Ocean could stimulate phytoplankton growth and the biological carbon pump. Some scientists believe that this process can partly explain cycles in atmospheric carbon dioxide over Earth's recent history and it has also been widely debated as a mitigation strategy for climate change.
>> Read the Full Article
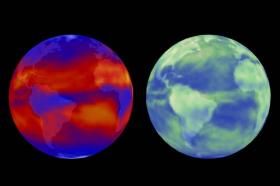
In classrooms and everyday conversation, explanations of global warming hinge on the greenhouse gas effect. In short, climate depends on the balance between two different kinds of radiation: The Earth absorbs incoming visible light from the sun, called “shortwave radiation,” and emits infrared light, or “longwave radiation,” into space.
Upsetting that energy balance are rising levels of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), that increasingly absorb some of the outgoing longwave radiation and trap it in the atmosphere. Energy accumulates in the climate system, and warming occurs. But in a paper out this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, MIT researchers show that this canonical view of global warming is only half the story.
>> Read the Full Article

Agriculture experts say application of alternate wetting and drying (AWD) technology in Vietnam’s rice farms, one of South-East Asia’s largest rice-producing countries, holds great promise in cutting water use and greenhouse gas emissions from rice cultivation without sacrificing yield output. Vietnam along with Bangladesh and Colombia recently partnered with the Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC) to introduce the large-scale application of AWD, also known as controlled irrigation in which farmers periodically drain rice paddies rather than keeping them perpetually flooded.
>> Read the Full Article

As one of the biking capitals of the world, Amsterdam can already make a case for being a leader in the green movement. The city is not resting on its laurels, however. Now, biking around the city is getting even greener than just being car-free: a bike path in the suburbs of Amsterdam is getting a major solar makeover.
>> Read the Full Article

The subject of making electric vehicles compulsory in city centres in the UK, and indeed many other areas of the world, is one which keeps popping up time and time again. The Liberal Democrat party in the UK has been pushing for greater adoption of electric vehicles within city centres and, don’t shout this, a ban on diesel and petrol vehicles. This is now something of a hot topic and one which will continue to appear in the political domain as we approach general and local elections.
How would you feel about making city centres a no-go area for petrol and diesel vehicles? Is electric vehicle technology of sufficient reliability to support such a dramatic and controversial move?
>> Read the Full Article

Thanks to the kindness of a caring citizen and the expertise of wildlife rehabilitators in Virginia, a common raven has been successfully returned to her home in the wild after being rescued and receiving months of care and a feather transplant.
The raven was first spotted by Maureen Bergin, an IT specialist at Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield earlier this spring in the parking lot where she worked in Henrico County with missing feathers that left her unable to fly.
>> Read the Full Article

Researchers from the Institute of Microbiology at ETH Zurich and the University of Bonn have discovered a new protein with antibiotic properties in a mushroom that grows on horse dung. The new agent that was found in fungi is found to kill bacteria. The substance, known as copsin, has the same effect as traditional antibiotics, but belongs to a different class of biochemical substances. Copsin is a protein, whereas traditional antibiotics are often non-protein organic compounds.
>> Read the Full Article

Protected areas are undoubtedly the world's most important conservation success story, and recent research shows that protected areas are effective—housing more biodiversity and greater abundances of species inside rather than out. But, despite this, progress on protected areas is stalling and in some cases even falling behind. According to a sobering new paper today in Nature, only 20-50 percent of the world's land and marine protected areas are meeting their goals, while the rest are hampered by lack of funding, poor management, and government ambivalence. The paper arrives just a few days before the opening of the IUCN World Parks Congress 2014, a global event that happens once a decade. "Protected areas offer us solutions to some of today's most pressing challenges, but by continuing with 'business as usual,' we are setting them up for failure," said lead author James Watson of the Wildlife Conservation Society and the University of Queensland. "A step-change in the way we value, fund, govern and manage those areas is neither impossible nor unrealistic and would only represent a fraction of what the world spends annually on defense."
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment