
Since hitching unsolicited rides in boat ballast water in the late 1980s, invasive quagga mussels (Dreissena rostriformis bugensis), which are native to Ukraine, have caused massive changes to the ecology of the Great Lakes. These invasive mussels have also taken a toll on the Great Lakes recreational and commercial fisheries, which are valued at $4-7 billion annually according to Michigan Sea Grant.
>> Read the Full Article

For two decades, environmentalist Jürgen Resch has locked horns with Germany’s mighty automobile industry, the backbone of Europe’s most powerful economy. And Resch has shown that he will do what Berlin’s top politicians won’t: hold carmakers — and German municipalities — to the letter of the law when it comes to the high levels of pollution spewed from diesel automobiles. His indispensable ally in this against-the-odds mission has been Germany’s court system.
>> Read the Full Article
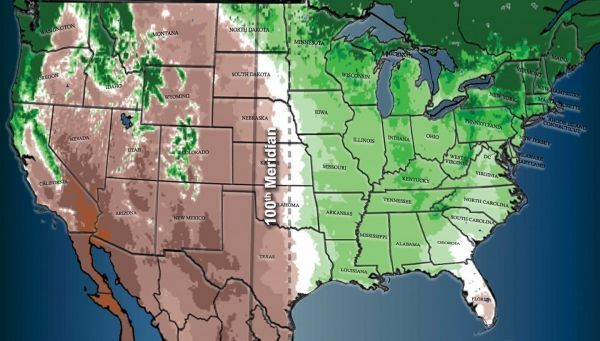
In 1878, the American geologist and explorer John Wesley Powell drew an invisible line in the dirt—a very long line. It was the 100th meridian west, the longitude he identified as the boundary between the humid eastern United States and the arid Western plains. Running south to north, the meridian cuts northward through the eastern states of Mexico, and on to Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, the Dakotas, and the Canadian province of Manitoba on its way to the pole. Powell, best known for exploring the Grand Canyon and other parts of the West, was wary of large-scale settlement in that often harsh region, and tried convincing Congress to lay out water and land-management districts crossing state lines to deal with environmental constraints. Western political leaders hated the idea—they feared this might limit development, and their own power—and it never went anywhere. It was not the first time that politicians would ignore the advice of scientists.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment