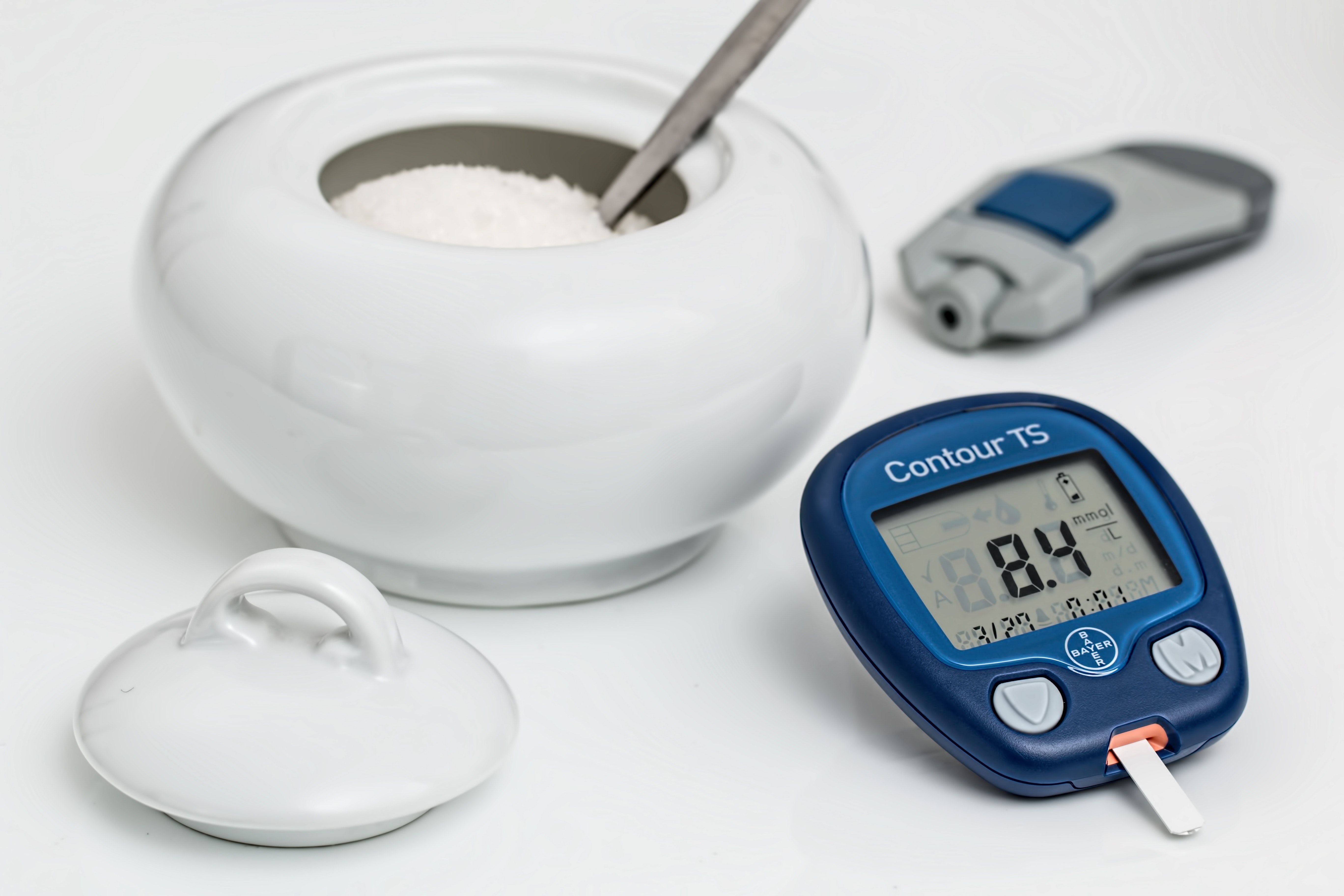
Mandatory nutrition policies could be a valuable tool in helping high school students to lower their sugar intake, a University of Waterloo study has found.
The study compared the consumption of sugar-sweetened drinks between 41,000 secondary school students in Ontario, where school nutrition policies are mandatory, and Alberta, where they are voluntary. The study took place during the 2013-14 school year.
>> Read the Full Article

The protection of our shared environment has long been among government’s most fundamental responsibilities. Ancient Rome’s Code of Justinian, one of the first efforts at constitutional governance, guaranteed to all citizens the use of the “public trust” or “commons” — those shared resources that cannot be reduced to private property, including the air, water, forests and fisheries. Throughout Western history, the first acts of tyrants have invariably included efforts to deliver public-trust assets into private hands. During the Dark Ages, when Roman law broke down in England, King John attempted to sell off the country’s fisheries, place navigational tolls on England’s rivers, and seize its woodlands and game animals. Enraged at that theft of public-trust assets, England’s people confronted John at Runnymede in 1215, forcing him to sign the Magna Carta. That seminal democratic document included a powerful articulation of the principle that the commons of water, fisheries and woodland were not commodities to be bartered away by a prince, but the rightful property of all citizens.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment