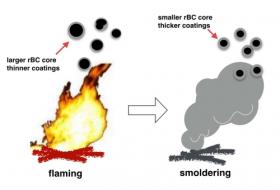
As a short-lived climate forcer, black carbon aerosols in the atmosphere play a vital role in climate change by absorbing solar radiation and altering the formation, lifespan and albedo of clouds. It also provides "seed" for haze formation in urban/regional scale. In northern China, open biomass burning (OBB), such as straw burning after harvesting, is one of important sources of refractory black carbon (rBC). OBB emits both soot particles and substantial amount of semi-volatile organic matters, both of which will undergo a very complicated mixing and evolution processes in the atmosphere to change their ability to form cloud condensation nuclei.
>> Read the Full Article

Surface water conditions in Greenland’s fjords and in the northern Atlantic Ocean are dictated by what’s going on deep below the surface next to the massive Greenland Ice Sheet, UO-led research has found.
Breakaway icebergs, according to research findings appearing online Dec. 4 ahead of publication in the journal Nature Geoscience, are the biggest source of freshwater entering the ocean in key areas around Greenland. And the timing and location of meltwater are important factors that should be included in ocean modeling, report the paper’s six co-authors.
>> Read the Full Article

China has released plans to create the world’s largest carbon emissions trading scheme, several news outlets reported. The market will initially be focused on the power sector, which produced almost half of the country’s greenhouse gas emissions last year, and will encompass 1,700 energy suppliers producing more than 3 billion tons of CO2 annually, according to Reuters.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment