
Humans have been altering natural waterways for centuries, but only in the last several decades have dams raised ecological concerns.
N. LeRoy Poff, professor of biology at Colorado State University, studies the ecological impact to rivers from human-caused changes, such as dam building, and how these modified river systems can be managed for resilience.
>> Read the Full Article

Canola oil is one of the most widely consumed vegetable oils in the world, yet surprisingly little is known about its effects on health. Now, a new study published online December 7 in the journal Scientific Reports by researchers at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University (LKSOM) associates the consumption of canola oil in the diet with worsened memory, worsened learning ability and weight gain in mice which model Alzheimer’s disease. The study is the first to suggest that canola oil is more harmful than healthful for the brain.
>> Read the Full Article
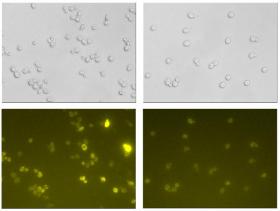
It took several years, but a research team headed by Professor Jens Nielsen at Chalmers University of Technology has finally succeeded in mapping out the complex metabolism of yeast cells. The breakthrough, recently published in an article in Nature Communications, means a huge step forward in the potential to more efficiently produce protein therapies for diseases such as cancer.
>> Read the Full Article

For millennia, the Beaufort Gyre — a massive wind-driven current in the Arctic Ocean — has been regulating climate and sea ice formation at the top of the world. Like a giant spinning top, the gyre corrals vast amounts of sea ice. Trapped in this clockwise swirl, the ice has historically had more time to thicken than it generally does in other parts of the Arctic Ocean, where currents such as the Trans Polar Drift transport the ice into the warmer north Atlantic more rapidly. In this way, the Beaufort Gyre — located north of Alaska and Canada’s Yukon Territory — has helped create the abundant layers of sea ice that, until recently, covered large parts of the Arctic Ocean year-round.
>> Read the Full Article

New research from the University of Michigan Life Sciences Institute has determined how a common holiday spice—cinnamon—might be enlisted in the fight against obesity.
Scientists had previously observed that cinnamaldehyde, an essential oil that gives cinnamon its flavor, appeared to protect mice against obesity and hyperglycemia. But the mechanisms underlying the effect were not well understood.
>> Read the Full Article

Shrinking glacier cover could lead to increased volcanic activity in Iceland, scientists have warned.
A new study, led by the University of Leeds, found there was less volcanic activity in Iceland when glacier cover was more extensive. As the glaciers melted, volcanic eruptions increased due to subsequent changes in surface pressure.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment