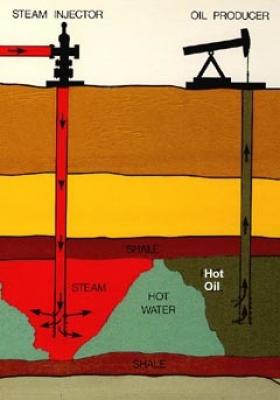
On New Year’s Day, 1909, a grocer named Julius Fried and his novice drilling crew, the Lakeview Oil Company, spudded a well in the desert valley scrub in the Midway-Sunset oil field, 110 miles north of Los Angeles. For the first 1,655 feet, the well yielded only dust, and then Lakeview ran out of money.
>> Read the Full Article

In 1995, the Governing Council of the United Nations Environment Program called for a united, global effort to reduce persistent organic pollutants (POPs) — synthetic chemicals such as PCBs, DDT, and dioxins. The compounds were known to persist and accumulate far from their sources, polluting the environment and causing adverse health effects in humans.
>> Read the Full Article

Tuna is one of the most ubiquitous seafoods. It can be eaten from a can or as high-end sashimi and in many forms in between. But some species are over-fished and some fishing methods are unsustainable. How do you know which type of tuna you’re eating?
Some tuna is certified as sustainably caught by groups such as the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) that set standards for sustainable fishing. But these certifications are only good if they are credible.
>> Read the Full Article

Forecasters at NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center released the U.S. Winter Outlook today, with La Nina potentially emerging for the second year in a row as the biggest wildcard in how this year’s winter will shape up. La Nina has a 55- to 65-percent chance of developing before winter sets in.
NOAA produces seasonal outlooks to help communities prepare for what's likely to come in the next few months and minimize weather's impacts on lives and livelihoods. Empowering people with actionable forecasts and winter weather tips is key to NOAA’s effort to build a Weather-Ready Nation.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment