
About half of atmospheric carbon dioxide is fixed by ocean's phytoplankton, mainly picocyanobacteria, through a process called photosynthesis. Picocyanobacteria are tiny, unicellular microorganisms that are abundant and widely distributed in freshwater and marine environments. A large portion of biologically fixed carbon is formed by picocyanobacteria at the sea surface and then transported to the deep ocean. But what remains a mystery is how colored dissolved organic matter which originates from plant detritus (either on land or at sea) makes it into the deep ocean. A team of scientists from the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science and around the world potentially found a viable marine source of this colored material.
>> Read the Full Article

Planting trees is a popular strategy to help make cities “greener,” both literally and figuratively. But scientists have found a counterintuitive effect of urban vegetation: During heat waves, it can increase air pollution levels and the formation of ozone. Their study appears in ACS’ journalEnvironmental Science & Technology.
Previous research has shown that planting trees in cities can have multiple benefits, including storing carbon, controlling storm water and cooling areas off by providing shade. This has spurred efforts in cities across the U.S. and Europe to encourage the practice. However, it’s also known that trees and other plants release volatile organic compounds, or VOCs, that can interact with other substances and contribute to air pollution. And when it’s hot, plants release higher levels of VOCs. Galina Churkina and colleagues wanted to investigate what effects heat waves and urban vegetation might have on air pollution.
>> Read the Full Article

At the Maji Agricultural Reservoir in Wonju, Gangwond-do, South Korea, that someone is Tae Kwon Lee. Lee regularly jogs around the reservoir. One day he noticed large black birds completely covering the small island in the lake. The black birds were great cormorants, a type of large water bird, and the trees on the islet were completely covered in the birds’ feces. As time passed, Lee made another observation: the lake suffered a severe algal bloom.
Algal blooms deplete oxygen in lakes, produce toxins, and end up killing aquatic life in the lake. This sequence of events got Lee wondering: Did the bird feces cause or contribute to the algal bloom?
>> Read the Full Article

The ocean sequesters massive amounts of carbon in the form of “dissolved organic matter,” and new research explains how an ancient group of cells in the dark ocean wrings the last bit of energy from carbon molecules resistant to breakdown.
A look at genomes from SAR202 bacterioplankton found oxidative enzymes and other important families of enzymes that indicate SAR202 may facilitate the last stages of breakdown before the dissolved oxygen matter, or DOM, reaches a “refractory” state that fends off further decomposition.
>> Read the Full Article
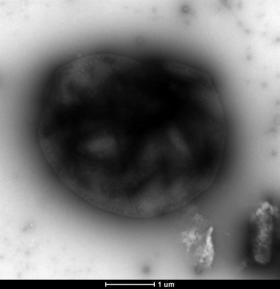
Transporting methane from gas wellheads to market provides multiple opportunities for this greenhouse gas to leak into the atmosphere. Now, an international team of researchers has taken the first step in converting methane directly to electricity using bacteria, in a way that could be done near the drilling sites.
"Currently, we have to ship methane via pipelines," said Thomas K. Wood, holder of the biotechnology endowed chair and professor of chemical engineering, Penn State. "When you ship methane, you release a greenhouse gas. We can't eliminate all the leakage, but we could cut it in half if we didn't ship it via pipe long distances."
The researchers' goal is to use microbial fuel cells to convert methane into electricity near the wellheads, eliminating long-distance transport. That goal is still far in the future, but they now have created a bacteria-powered fuel cell that can convert the methane into small amounts of electricity.
>> Read the Full Article

Imagine you’re swimming lazily along, just below the water’s surface in a tropical ocean. You look down at a colorful array of pinks, yellows and greens. Spikey corals cover the floor below. Small fish swim in and out of hiding places, ducking behind the stationary animals to avoid your peering eyes.
>> Read the Full Article

Ormia ochracea's sense of directional hearing is second to none in the animal kingdom.
“These flies have highly specialized ears that provide the most acute directional hearing of any animal,” says Andrew Mason, an associate professor of biology at U of T Scarborough. “The mechanism that makes their hearing so exceptional has even led to a range of bio-inspired technology, like the mini-directional microphones used in hearing aids.”
>> Read the Full Article

Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed the first soft robot that is capable of walking on rough surfaces, such as sand and pebbles. The 3D-printed, four-legged robot can climb over obstacles and walk on different terrains.
Researchers led by Michael Tolley, a mechanical engineering professor at the University of California San Diego, will present the robot at the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation from May 29 to June 3 in Singapore. The robot could be used to capture sensor readings in dangerous environments or for search and rescue.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment