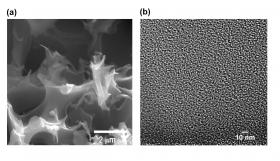
Natural gas producers want to draw all the methane they can from a well while sequestering as much carbon dioxide as possible, and could use filters that optimize either carbon capture or methane flow. No single filter will do both, but thanks to Rice University scientists, they now know how to fine-tune sorbents for their needs.
Subtle adjustments in the manufacture of a polymer-based carbon sorbent make it the best-known material either for capturing the greenhouse gas or balancing carbon capture with methane selectivity, according to Rice chemist Andrew Barron.
>> Read the Full Article
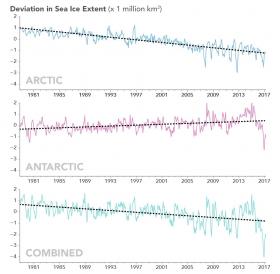
Arctic sea ice appears to have reached on March 7 a record low wintertime maximum extent, according to scientists at NASA and the NASA-supported National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) in Boulder, Colorado. And on the opposite side of the planet, on March 3 sea ice around Antarctica hit its lowest extent ever recorded by satellites at the end of summer in the Southern Hemisphere, a surprising turn of events after decades of moderate sea ice expansion.
On Feb. 13, the combined Arctic and Antarctic sea ice numbers were at their lowest point since satellites began to continuously measure sea ice in 1979. Total polar sea ice covered 6.26 million square miles (16.21 million square kilometers), which is 790,000 square miles (2 million square kilometers) less than the average global minimum extent for 1981-2010 – the equivalent of having lost a chunk of sea ice larger than Mexico.
>> Read the Full Article

In the South China Sea, a 2°C rise in the sea surface temperature in June 2015 was amplified to produce a 6°C rise on Dongsha Atoll, a shallow coral reef ecosystem, killing approximately 40 percent of the resident coral community within weeks, according to a study published in Scientific Reports this week.
Wind and waves churn the sea, flushing shallow-water coral reefs with seawater from the open ocean to help them stay cool. But according to new research from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), when the weather turns still and these natural cooling mechanisms subside, just a few degrees of ocean warming can prove lethal to the corals that live there.
>> Read the Full Article

Google Street View cars have driven millions of miles across the globe, capturing 360-degree images of roadways and communities on all seven continents. Now, scientists and environmentalists are teaming up to add pollution trackers to the vehicles so they can monitor natural gas leaks as they drive.
The new project, detailed this week in the journal Environmental Science and Technology, is being led by researchers at Colorado State University, the Environmental Defense Fund, and Google Earth Outreach.
>> Read the Full Article
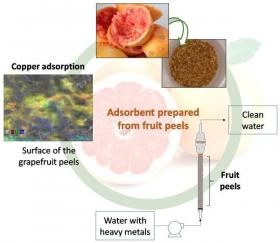
Researchers from the University of Granada (UGR), and from the Center for Electrochemical Research and Technological Development (Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo Tecnológico en Electroquímica, CIDETEQ) and the Center of Engineering and Industrial Development (Centro de Ingeniería y Desarrollo Industrial, CIDESI), both in Mexico, have developed a process that allows to clean waters containing heavy metals and organic compounds considered pollutants, using a new adsorbent material made from the peels of fruits such as oranges and grapefruits.
>> Read the Full Article

Among ecologists, carbon gets all the glory. Scientists examine its critical role in plant growth and decay, they chart its contributions to greenhouse gases, and they measure its sequestration in earth, sea, and sky.
Often overlooked in all this research is the humble element silicon, or “silica,” as it’s called when found in nature. If ecologists (or biologists or biogeochemists) think of silica at all, they regard it as a bit player, a ho-hum component of rocks and sand.
>> Read the Full Article

The hills of West Texas rise in waves around the Hobby-Eberly Telescope, a powerful instrument encased in a dome that looks like the Epcot ball. Soon, it will become more powerful still: Scientists recently primed the telescope to find evidence of dark energy in the early universe, prying open its eye so it can see and process a wide swath of sky. On April 8, scientists will dedicate the new telescope, capping off the $40 million upgrade and beginning the real work.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment