
Most modern websites store data in databases, and since database queries are relatively slow, most sites also maintain so-called cache servers, which list the results of common queries for faster access. A data center for a major web service such as Google or Facebook might have as many as 1,000 servers dedicated just to caching.
>> Read the Full Article

As of this morning, 57 USGS streamgages are over National Weather Service flood levels, and water continues to rise at 118 gauges throughout Texas.
Seventeen USGS field crews are measuring high flood flows and verifying streamgage operations on the Colorado, Brazos, San Jacinto and Trinity River basins. Preliminary data show record high flood levels were measured at 16 locations throughout the greater Houston area. Accessing specific locations has proved challenging due to road closures and many sites being flooded at levels too dangerous to measure at this time.
>> Read the Full Article

Ocean acidification can be a daunting topic to cover in the classroom, but for Washington state’s coastal communities, the issue is often personal.
Ocean acidification can be a daunting topic to cover in the classroom, but for Washington state’s coastal communities, the issue is often personal. In 2005, billions of oysters died along the Northwest coast, and NOAA scientist Richard Feeley and other North American scientists have linked this and other shellfish die-offs deaths to falling ocean pH1. According to Washington State’s Blue Ribbon Panel on Ocean Acidification, Washington’s ocean waters are specifically susceptible to ocean acidification because of coastal upwelling. This brings water that is low in pH and rich in carbon dioxide up from the deep ocean and onto the continental shelf. Ocean acidification, also exacerbated by nutrient runoff and local carbon emissions, threatens Washington’s marine environment, the state and local economies, and tribes.
>> Read the Full Article

Although Midwestern soybean growers have yet to experience the brunt of soybean rust, growers in the southern United States are very familiar with the disease. Every year, the fungus slowly moves northward from its winter home in southern Florida and the Gulf Coast states, and eventually reaches Illinois soybean fields—often just before harvest.
>> Read the Full Article

Houston has been a hub of the petroleum and chemical industries for decades, leaving behind a landscape pocked with Superfund sites and other highly contaminated areas. Now, scientists are warning that these sites are likely leaking toxins into Tropical Storm Harvey’s floodwaters, exposing people in Harris County, where 30 percent of the land is now submerged, to dangerous contaminants, The Washington Post reported.
>> Read the Full Article
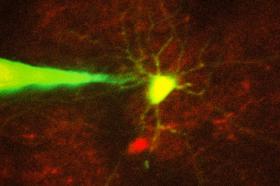
Recording electrical signals from inside a neuron in the living brain can reveal a great deal of information about that neuron’s function and how it coordinates with other cells in the brain. However, performing this kind of recording is extremely difficult, so only a handful of neuroscience labs around the world do it.
To make this technique more widely available, MIT engineers have now devised a way to automate the process, using a computer algorithm that analyzes microscope images and guides a robotic arm to the target cell.
>> Read the Full Article
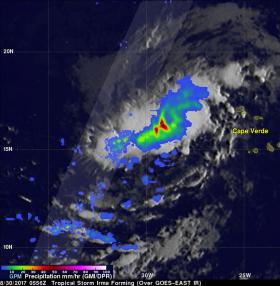
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) upgraded a low pressure area in the far eastern Atlantic Ocean to tropical storm Irma on August 30, 2017 at 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC).
Tropical cyclones that form in that part of the Atlantic Ocean are often the largest and most powerful hurricanes of the season. Hurricanes Ivan (2004), Isabel (2003), Hugo (1989) and Allen (1980) are examples of past powerful hurricanes that formed near the Cape Verde islands.
>> Read the Full Article

When the Fukushima power plant released large quantities of radioactive materials into nearby coastal waters following Japan’s massive 2011 earthquake and tsunami, it raised concerns as to whether eating contaminated seafood might impair human health—not just locally but across the Pacific.
A new study by an international research team shows that those concerns can now be laid to rest, at least for consumption of meat from migratory marine predators such as tuna, swordfish, and sharks.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment