
If coastal salt marshes are like savings accounts, with sediment as the principal, all eight Atlantic and Pacific coast salt marshes studied are "in the red," researchers found.
Scientists working on a rapid assessment technique for determining which US coastal salt marshes are most imperiled by erosion were surprised to find that all eight of the Atlantic and Pacific Coast marshes where they field-tested their method are losing ground, and half of them will be gone in 350 years’ time if they don’t recapture some lost terrain.
>> Read the Full Article

Since the GOES-16 satellite lifted off from Cape Canaveral on November 19, scientists, meteorologists and ordinary weather enthusiasts have anxiously waited for the first photos from NOAA’s newest weather satellite, GOES-16, formerly GOES-R.
The release of the first images today is the latest step in a new age of weather satellites. It will be like high-definition from the heavens.
>> Read the Full Article

Tesla has always been about pushing full speed toward a tech-tastic future. CEO Elon Musk wouldn’t settle for making a luxurious, sexy, environmentally-friendly electric car. He made one that could hit 60 mph in 3.2 seconds. Then 2.8 seconds. Then 2.5—all the while ratcheting up the range, from the original 265 miles per charge to the current, top of the line 335.
>> Read the Full Article

As Friday night became Saturday morning, Dong Kim sounded defeated.
Kim is a high-stakes poker player who specializes in no-limit Texas Hold ‘Em. The 28-year-old Korean-American typically matches wits with other top players on high-stakes internet sites or at the big Las Vegas casinos. But this month, he’s in Pittsburgh, playing poker against an artificially intelligent machine designed by two computer scientists at Carnegie Mellon. No computer has ever beaten the top players at no-limit Texas Hold ‘Em, a particularly complex game of cards that serves as the main event at the World Series of Poker. Nearly two years ago, Kim was among the players who defeated an earlier incarnation of the AI at the same casino. But this time is different. Late Friday night, just ten days into this twenty-day contest, Kim told me that he and his fellow humans have no real chance of winning.
>> Read the Full Article

It is really hard to photograph a meteor. Even though some 25 million of them hurtle toward Earth each day, most of them are too small to track. Those you can see are tough to spot during the day, and most people are sleeping when they streak across the sky at night. But Prasenjeet Yadav managed to get one anyway, entirely by accident.
>> Read the Full Article

After a flock of Canada geese knocked out the engines of a US Airways jetliner in January 2009, pilot “Sully” Sullenberger was famously able to safely land the Airbus A320 on the Hudson River. What became known as the “Miracle on the Hudson” was happy news, especially for the 155 passengers whose lives Sullenberger saved.
But it was terrible news for geese and other birds that migrate or make their homes near the three major airports in the New York City area. To prevent a similar incident from happening again, nearly 70,000 birds have been intentionally killed near John F. Kennedy, LaGuardia and Newark airports over the past eight years, the Associated Press reports.
>> Read the Full Article

Cornell engineers hope that clean water runs deep. They have developed a new technique to test for a wide range of micropollutants in lakes, rivers and other potable water sources that vastly outperforms conventional methods.
“Water quality monitoring is conventionally done by narrowly investigating one or a few contaminants at a time. We aimed to develop an analytical method that would be as broad as possible,” said Damian Helbling, assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering. Helbling and Amy Pochodylo, M.S. ’14, published their research as the cover story in the journal Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology.
>> Read the Full Article
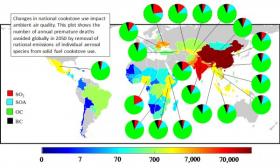
New air quality research is investigating a major, but often overlooked contributor to outdoor pollution and climate: burning of solid fuel for cooking and heating.
Cookstove studies typically evaluate how they contribute to indoor air quality issues in houses where solid fuel is frequently used for cooking and heating. A new paper from the University of Colorado Boulder appearing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, has taken a different approach, going outside the home and evaluating how cookstoves impact ambient air pollution and climate.
>> Read the Full Article
Physicist Fatima Ebrahimi at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) has published a paper showing that magnetic reconnection — the process in which magnetic field lines snap together and release energy — can be triggered by motion in nearby magnetic fields. By running computer simulations, Ebrahimi gathered evidence indicating that the wiggling of atomic particles and magnetic fields within electrically charged gas known as plasma can spark the onset of reconnection, a process that, when it occurs on the sun, can spew plasma into space.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment