
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is an important greenhouse gas that doesn’t receive as much notoriety as carbon dioxide or methane, but a new study confirms that atmospheric levels of N2O rose significantly as the Earth came out of the last ice age and addresses the cause.
An international team of scientists analyzed air extracted from bubbles enclosed in ancient polar ice from Taylor Glacier in Antarctica, allowing for the reconstruction of the past atmospheric composition. The analysis documented a 30 percent increase in atmospheric nitrous oxide concentrations from 16,000 years ago to 10,000 years ago. This rise in N2O was caused by changes in environmental conditions in the ocean and on land, scientists say, and contributed to the warming at the end of the ice age and the melting of large ice sheets that then existed.
>> Read the Full Article

Ron Patalano, director of operations at Roger Williams Park Zoo, has high praise for his staff. After all, it takes a mighty amount of shoveling to fill the two 30-yard Dumpsters of animal excrement that are hauled away weekly as part of the zoo’s recycling program.
Added to the grass clippings, vegetable scraps, animal bedding, hay and other natural materials trucked to Earth Care Farm in Charleston for composting, are 624 tons of manure produced annually by the zoo’s 280 inhabitants.
Keeping yards and buildings waste free “is not an easy job,” Patalano noted.
The zoo’s relationship with Earth Care Farm — Rhode Island’s longtime composting mecca — goes back at least 15 years, according to John Barth, the farm’s manager.
>> Read the Full Article

In the battle between native and invasive wetland plants, a new Duke University study finds climate change may tip the scales in favor of the invaders -- but it's going to be more a war of attrition than a frontal assault.
"Changing surface-water temperatures, rainfall patterns and river flows will likely give Japanese knotweed, hydrilla, honeysuckle, privet and other noxious invasive species an edge over less adaptable native species," said Neal E. Flanagan, visiting assistant professor at the Duke Wetland Center, who led the research.
>> Read the Full Article

Princeton University researchers have uncovered a previously unknown, and possibly substantial, source of the greenhouse gas methane to the Earth's atmosphere. After testing a sample of abandoned oil and natural gas wells in northwestern Pennsylvania, the researchers found that many of the old wells leaked substantial quantities of methane.
>> Read the Full Article
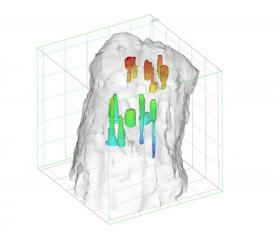
Large-scale storage of low-pressure, gaseous hydrogen in salt caverns and other underground sites for transportation fuel and grid-scale energy applications offers several advantages over above-ground storage, says a recent Sandia National Laboratories study sponsored by the Department of Energy’s Fuel Cell Technologies Office.
Geologic storage of hydrogen gas could make it possible to produce and distribute large quantities of hydrogen fuel for the growing fuel cell electric vehicle market, the researchers concluded.
Geologic storage solutions can service a number of key hydrogen markets since “costs are more influenced by the geology available rather than the size of the hydrogen market demand,” said Sandia’s Anna Snider Lord, the study’s principal investigator.
>> Read the Full Article

Natural gas power plants produce substantial amounts of gases that lead to global warming. Replacing old coal-fired power plants with new natural gas plants could cause climate damage to increase over the next decades, unless their methane leakage rates are very low and the new power plants are very efficient.
These are the principal findings of new research from Carnegie’s Ken Caldeira and Xiaochun Zhang, and Nathan Myhrvold of Intellectual Ventures that compares the temperature increases caused by different kinds of coal and natural gas power plants. Their work is published in Environmental Research Letters.
>> Read the Full Article

Today, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is launching its Energy Star Home Advisor, an online tool designed to help Americans save money and energy by improving the energy efficiency of their homes through recommended, customized and prioritized home-improvement projects.
>> Read the Full Article

The majority of streams in the Chesapeake Bay region are warming, and that increase appears to be driven largely by rising air temperatures. These findings are based on new U.S. Geological Survey research published in the journal Climatic Change.
Researchers found an overall warming trend in air temperature of 0.023 C (0.041 F) per year, and in water temperature of 0.028 C (0.050 F) per year over 51 years. This means that air temperature has risen 1.1 C (1.98 F), and water temperature has risen 1.4 C (2.52 F) between 1960 and 2010 in the Chesapeake Bay region.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment