
As the International Commission for the Conservation of Atlantic Tunas (ICCAT) opens its 19th special meeting in Genoa, Italy on Monday 10 November, WWF calls on delegates to stay cautious regarding the management of Mediterranean bluefin tuna. Despite recent indications that the stock is recovering, substantial shortcomings still undermine traceability of the fishery, allowing for illegal, unreported and unregulated (IUU) bluefin tuna to reach global markets.
>> Read the Full Article

Man has been amazed by comets for millenia. What are they, these beautiful wanderers? There have been many theories, the most popular being that they are balls of ice. Now we are actually getting data. The photographs taken by the European Space Agency's Rosetta spacecraft show comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko to be more rocklike than a ball of ice.
After sailing through space for more than 10 years, the Rosetta spacecraft is now less than a week shy of landing a robotic probe on a comet.
The mission's Philae (fee-LAY) lander is scheduled to touch down on comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko on Wednesday, Nov. 12 at 7:35 a.m PST/10:35 a.m. EST. A signal confirming the landing is expected about 8:02 a.m. PST/11:02 a.m. EST. If all goes as planned with this complex engineering feat, it will be the first-ever soft landing of a spacecraft on a comet.
>> Read the Full Article

We all know that greenhouse gases contribute to global warming, but new research identifies a new mechanism that could turn out to be a major contributor to melting sea ice, specifically in the Arctic region. Scientists from the US Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have studied a long-wavelength region of the electromagnetic spectrum called far infrared. Far infrared is a region in the infrared spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. While it is invisible to our eyes, it accounts for about half the energy emitted by the Earth’s surface.
>> Read the Full Article

In 2008, Danny Swan was a junior at Jesuit University in Wheeling, West Virginia. The town was a shadow of its former self as a thriving hub for the coal and steel industries. As America turned to more green energy and offshore production, jobs and people abandoned the town. Left behind were abandoned buildings, crime and a depressed community.
Danny Swan spent his time between classes gardening in the backyard of the university residence he lived in and volunteering at an after-school program for inner-city kids. He was in search of a way to expand the concrete urban world of the children he worked with. His solution was found right across the street from the chapel that housed the program, underneath a highway overpass.
>> Read the Full Article

A majority of recent reports highlights the negative effects of warmer water temperatures on corals. Because of increasing numbers of bleaching events, where corals become white resulting from a loss of their symbiotic algae, corals become stressed and can starve to death if the condition is prolonged. However, researchers from Northeastern University's Marine Science Center and the University of Chapel Hill have found some slightly positive effects that moderate ocean acidification and warming can have on coral.
>> Read the Full Article
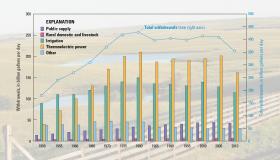
Water use across the country reached its lowest recorded level in nearly 45 years. According to a new USGS report, about 355 billion gallons of water per day (Bgal/d) were withdrawn for use in the entire United States during 2010.
This represents a 13 percent reduction of water use from 2005 when about 410 Bgal/d were withdrawn and the lowest level since before 1970.
“Reaching this 45-year low shows the positive trends in conservation that stem from improvements in water-use technologies and management,” said Mike Connor, deputy secretary of the Interior. “Even as the U.S. population continues to grow, people are learning to be more water conscious and do their part to help sustain the limited freshwater resources in the country.”
>> Read the Full Article

A group of scientists working in collaboration with a filmmaker have come up with a clever, and adorable, way to study notoriously shy Emperor penguins in Adélie Land, Antarctica by sending in a rover disguised as a chick that was so convincing penguins tried to make conversation with it. As researchers explain in a study published in the journal Nature Methods, which was led by Yvon Le Maho of the University of Strasbourg in France, scientists have been unable to study these penguins up close without seriously stressing them out, altering their behavior or causing them to retreat.
>> Read the Full Article

If we are to believe much of what we see in the press, millennials will have to make a more sustainable world to get us out of the mess that the baby boomers are leaving behind. But such generalities may not be necessarily true. Even AARP, which has paid plenty of attention to the baby boomer vs. millennials conflict, has made the case that its membership is concerned about the same issues with which the younger generation is often preoccupied. For example, one may not intuitively think of AARP as a locus of information on smart cities and better urban planning. This powerful lobbying group, however, has an impressive archive that inspires its members to advocate for more “liveable communities.”
>> Read the Full Article

In many ways electric car technology jumped to far too quickly leaving behind electric vehicle charging systems which for many years have been totally inadequate. There has been major concern amongst motorists around the world that even the most technologically advanced electric vehicle would be unreliable if you are not able to charge it when and where you wanted. This has held the electric car industry for some time although thankfully governments around the world are now focusing upon electric car charging networks.
This then begs the question – could electric car chargers be the next growth industry?
>> Read the Full Article

Naturally occurring asbestos minerals may be more widespread than previously thought, with newly discovered sources now identified within the Las Vegas metropolitan area. The asbestos-rich areas are in locations not previously considered to be at risk, according to new report that will be presented at the Annual Meeting of the Geological Society of America (GSA) in Vancouver, Canada, on Sunday, 20 October.
"These minerals were found where one wouldn't expect or think to look," said Rodney Metcalf, associate professor of geology at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, and co-researcher of the study. The naturally occurring asbestos was found in Boulder City, Nevada, in the path of a construction zone to build a multi-million dollar highway called the Boulder City Bypass, the first stage of an I-11 corridor planned between Las Vegas and Arizona.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment