
With warm, dry summers comes a deadly caveat for the western United States: wildfires. Scientists say the hot, dry climates found west of the Mississippi, along with decades of fire suppression efforts, are creating a devastating and destructive combination – leading to fires like the ones currently burning in California.
>> Read the Full Article

A new study linking paleoclimatology — the reconstruction of past global climates — with historical analysis by researchers at Yale and other institutions shows a link between environmental stress and its impact on the economy, political stability, and war-fighting capacity of ancient Egypt.
The team of researchers examined the hydroclimatic and societal impacts in Egypt of a sequence of tropical and high-latitude volcanic eruptions spanning the past 2,500 years, as known from modern ice-core records. The team focused on the Ptolemaic dynasty of ancient Egypt (305-30 B.C.E.) — a state formed in the aftermath of the campaigns of Alexander the Great, and famed for rulers such as Cleopatra — as well as material and cultural achievements including the great Library and Lighthouse of Alexandria.
>> Read the Full Article

An international research team, including physicists from the Weizmann Institute of Science, has for the first time succeeded in observing a merger of two colliding neutron stars. The merger was simultaneously picked up by three detectors built for this purpose: the two belonging to the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory, or LIGO, in the United States, and the Virgo detector in Italy. The observation may help determine how such heavy elements as uranium, iodine and gold were formed and enhance our understanding of some of the most violent events in the history of the universe.
>> Read the Full Article

Around 245 BCE Ptolemy III, ruler of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt, made a decision that still puzzles many historians: After pursuing a successful military campaign against the kingdom’s nemesis, the Seleucid Empire, centred mainly in present-day Syria and Iraq, the king suddenly decided to return home. This about-face “changed everything about Near-East history,” says Joseph Manning, a historian at Yale University.
>> Read the Full Article

On May 29, 2006, mud started erupting from several sites on the Indonesian island of Java. Boiling mud, water, rocks and gas poured from newly-created vents in the ground, burying entire towns and compelling many Indonesians to flee. By September 2006, the largest eruption site reached a peak, and enough mud gushed on the surface to fill 72 Olympic-sized swimming pools daily.
>> Read the Full Article
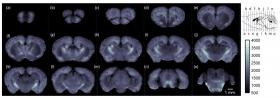
An estimated 5.5 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, a type of dementia that causes problems with memory, thinking and behavior. Although treatments can slow the worsening of symptoms, scientists are still working to better understand the neurodegenerative disease so that curative and preventative medicines can be developed. A new imaging system could help speed new drug development by offering a better way to monitor the brain changes indicative of Alzheimer’s in mouse models of the disease.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment