
Flowering crops such as beans and cotton offer their sweetest nectar to recruit colonising ants.
This strategy balances their need for defence and to reproduce, research suggests.
So-called ant-plants carefully manage the amount and sweetness of nectar produced on their flowers and leaves, a study shows.
This enables them to attract ants – which aggressively deter herbivores – while also luring insects that will spread pollen.
>> Read the Full Article

During the last glacial period, within only a few decades the influence of atmospheric CO2 on the North Atlantic circulation resulted in temperature increases of up to 10 degrees Celsius in Greenland – as indicated by new climate calculations from researchers at the Alfred Wegener Institute and the University of Cardiff. Their study is the first to confirm that there have been situations in our planet’s history in which gradually rising CO2 concentrations have set off abrupt changes in ocean circulation and climate at “tipping points”. These sudden changes, referred to as Dansgaard-Oeschger events, have been observed in ice cores collected in Greenland. The results of the study have just been released in the journal Nature Geoscience.
>> Read the Full Article

Like driving a car despite a glowing check-engine light, large buildings often chug along without maintenance being performed on the building controls designed to keep them running smoothly.
And sometimes those controls aren't used to their full potential, similar to a car at high speed in first gear. Instead of an expensive visit to the mechanic, the result for a commercial building is a high power bill.
A new report finds that if commercial buildings fully used controls nationwide, the U.S. could slash its energy consumption by the equivalent of what is currently used by 12 to 15 million Americans.
>> Read the Full Article

In the popular children’s story “Horton Hears a Who!” author Dr. Seuss tells of a gentle and protective elephant who stumbles upon a speck of dust that harbors a community of microscopic creatures called the Whos living the equally tiny town of Whoville. Throughout their journey together, Horton argues for the existence of the Whos traveling around in the air on a dust speck, while doubters dispute the finding. Ultimately, through observation, evidence for the organisms emerges, but regardless of the outcome, this speck altered a world greater than its own.
While this tale is a work of fiction, climate and atmospheric scientists have considered a real-life Whoville scenario — biological particles and inorganic material riding around in the atmosphere affecting the climate. Previous research has shown that some aerosols are very good at nucleating ice, which could form clouds in the troposphere. But due to complex atmospheric chemistries and a lack of data, scientists aren’t sure what percentage of these ice active particles are biological in nature and abundant enough in the troposphere to have an impact on climate. Furthermore, chemically parsing the metaphorical Whos from their speck has proved difficult — until now.
>> Read the Full Article

Prairie dogs in the wild are less likely to succumb to plague after they ingest peanut-butter-flavored bait that contains a vaccine against the disease, according to a U.S. Geological Survey study published today in the journal EcoHealth.
In an effort to increase populations of endangered black-footed ferrets and conserve the prairie dogs they rely on for survival, it is essential for land managers to control outbreaks of the bacterial disease also known as sylvatic plague. The plague affects numerous wild animal species, and domestic animals and humans are susceptible as well.
>> Read the Full Article

Coastal communities are struggling with the complex social and ecological impacts of a growing global hunger for a seafood delicacy, according to a new study from the University of British Columbia.
“Soaring demand has spurred sea cucumber booms across the globe,” says lead author Maery Kaplan-Hallam, who conducted the research as a master’s student with the Institute for Resources, Environment and Sustainability (IRES) at UBC.
>> Read the Full Article
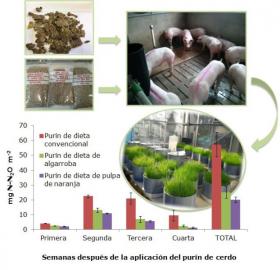
A research of UPM and UPV has shown that the inclusion of agroindustrial by-products in pig feed can reduce the nitrous oxide emissions (N2O) of the slurry used as manures up to 65%.
The aim of this study carried out by UPM researchers with the collaboration of Institute for Animal Science and Technology of UPV was to influence the ingredients of pig diet to modify the composition of slurry used as manures and to assess the possible variations on N2O emissions.
>> Read the Full Article
A team of scientists led by the Universities of Leicester and East Anglia are leading research to protect wildlife by using satellite data to identify monkey populations that have declined through hunting.
In a new article in the journal Nature Ecology and Evolution, a working group chaired by Professor Heiko Balzter, from the National Centre for Earth Observation at the University of Leicester, has looked at ways in which an array of technologies could be used to identify how many species are alive in an area and the risks they may be exposed to.
>> Read the Full Article
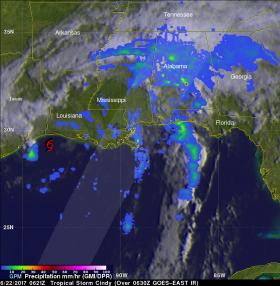
NASA's Aqua satellite analyzed Tropical Storm Cindy in infrared light to identify areas of strongest storms and the Global Precipitation Measurement mission or GPM satellite found locations of heaviest rainfall as Cindy was making landfall along the U.S. Gulf Coast states.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite looked at Tropical Depression Cindy in infrared light. The AIRS image was taken on June 21 at 19:53 UTC (3:53 p.m. EST) and showed some cloud top temperatures of thunderstorms near the center of circulation as cold as minus 63 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 53 degrees Celsius). NASA research has shown the storms with cloud tops that cold have the potential to generate heavy rainfall.
The infrared data was false-colored at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, where AIRS data is managed.
Cindy made landfall around 3 a.m. CDT in southwestern Louisiana. At that time, the National Hurricane Center or NHC said that Cindy was centered about 30 miles (45 km) west-southwest of Lake Charles, Louisiana.
>> Read the Full Article

Scientists have developed a new low-temperature catalyst for producing high-purity hydrogen gas while simultaneously using up carbon monoxide (CO). The discovery—described in a paper set to publish online in the journal Science on Thursday, June 22, 2017—could improve the performance of fuel cells that run on hydrogen fuel but can be poisoned by CO.
“This catalyst produces a purer form of hydrogen to feed into the fuel cell,” said José Rodriguez, a chemist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory. Rodriguez and colleagues in Brookhaven’s Chemistry Division—Ping Liu and Wenqian Xu—were among the team of scientists who helped to characterize the structural and mechanistic details of the catalyst, which was synthesized and tested by collaborators at Peking University in an effort led by Chemistry Professor Ding Ma.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment