
A concentrating photovoltaic system with embedded microtracking can produce over 50 percent more energy per day than standard silicon solar cells in a head-to-head competition, according to a team of engineers who field tested a prototype unit over two sunny days last fall.
"Solar cells used to be expensive, but now they're getting really cheap," said Chris Giebink, Charles K. Etner Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering, Penn State. "As a result, the solar cell is no longer the dominant cost of the energy it produces. The majority of the cost increasingly lies in everything else — the inverter, installation labor, permitting fees, etc. — all the stuff we used to neglect."
>> Read the Full Article

A study in the Marcellus Shale region of western Pennsylvania has shown that even after being treated, wastewater from hydraulic fracturing operations left significant contamination in a waterway downstream of treatment plants.
Researchers from Penn State University, Colorado State University, and Dartmouth College studied sediments from Conemaugh River Lake — a dammed reservoir east of Pittsburgh — and found that they were contaminated with endocrine-disrupting chemicals called nonylphenol ethoxylates; polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which are carcinogens; and elevated levels of radium.
>> Read the Full Article

Forest birds on the island of Hawaii are responding positively to being restored in one of the largest, ongoing reforestation projects at Hakalau Forest National Wildlife Refuge, according to a new study released July 10 in the journal Restoration Ecology.
Serving as pollinators and seed dispersers, birds have an important role in ecosystem function and their presence in restoration areas can be a measure of success for conservation efforts.
>> Read the Full Article

An international research team has discovered that anywhere from 25 to 100 billion failed stars reside in the Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way Galaxy is the celestial home to Earth.
The failed stars, which are known as Brown dwarfs, are astronomical entities that are too large to be planets and too small to be stars.
>> Read the Full Article
Autonomous robots can inspect nuclear power plants, clean up oil spills in the ocean, accompany fighter planes into combat and explore the surface of Mars.
Yet for all their talents, robots still can’t make a cup of tea.
That’s because tasks such as turning the stove on, fetching the kettle and finding the milk and sugar require perceptual abilities that, for most machines, are still a fantasy.
>> Read the Full Article
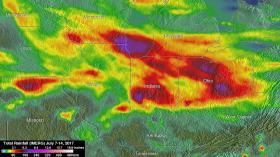
Heavy rain resulted in significant flooding in the U.S. Midwest over the week of July 7 to 14, 2017. Using satellite data, NASA estimated the amount of rain that fell over those areas and used satellite data to create 3-D imagery of severe storms.
NASA's Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) data were used to show estimates of rainfall accumulation in the Midwest during the period from July 7 to 14, 2017. The analysis was conducted at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and indicates that parts of Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana and Ohio had the highest rainfall totals during the period with more than 6 inches (152.4 mm) of rain being seen in many areas.
>> Read the Full Article
A new algorithm developed by Stanford computer scientists can sift through hours of heart rhythm data generated by some wearable monitors to find sometimes life-threatening irregular heartbeats, called arrhythmias. The algorithm, detailed in an arXiv paper, performs better than trained cardiologists, and has the added benefit of being able to sort through data from remote locations where people don’t have routine access to cardiologists.
>> Read the Full Article

Four out of 10 Americans live in “double whammy” counties where unhealthy smog and pollen-producing ragweed– both tied to the growing climate crisis – combine to threaten respiratory health, a Natural Resources Defense Council mapping project released today shows.
NRDC’s analysis found air quality “hot spots” in states and areas with the greatest percentages of people living in areas with both ragweed and unhealthy ozone days. Ironically, Washington, D.C., -- where climate action is being rolled back — leads the rankings followed by Connecticut, Rhode Island, Illinois and Pennsylvania.
127 million Americans live in zones where increased carbon dioxide and ozone smog pollution largely from burning fossil fuels, combined with more ragweed pollen, can worsen respiratory allergies and asthma. That can lead to more sick days, higher medical costs, and a rise in the number of heart problems and premature deaths each year.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment