
An international collaboration involving the Earlham Institute, Norwich, UK, and the Iwate Biotechnology Research Centre, Japan, has for the first time provided a genome sequence for the white Guinea yam, a staple crop with huge economic and cultural significance on the African continent and a lifeline for millions of people.
>> Read the Full Article
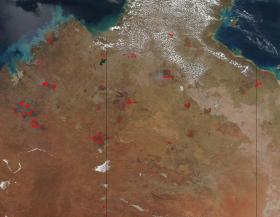
Fires that span across the Northern Territory and Western Australia appear to have broken out in areas that have already been burned in previous fires. Areas that sport "burn scars", those areas that are a darker, almost red-brown color, are surrounded by fires that are anywhere from a few hours old to 7 days old. The areas that are seven days old can be attributed to fires that spread but areas that are just a few hours old may be fires that have presumably been put out only to have them break out again. The Northern Territory of Australia experienced a higher than normal amount of rain this past season allowing the plants and trees that fuel fires to become even more overgrown and subject to becoming fire fodder.
>> Read the Full Article
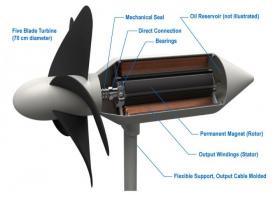
Professor Tsumoru Shintake at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) yearns for a clean future, one that is affordable and powered by sustainable energy. Originally from the high-energy accelerator field, in 2012 he decided to seek new energy resources—wind and solar were being explored in depth, but he moved toward the sea instead.
>> Read the Full Article

Outdoor air pollution has long been linked to major health conditions such as heart disease, stroke, cancer, asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A new study now adds kidney disease to the list, according to researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the Veterans Affairs (VA) St. Louis Health Care System.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment