
Scientists from the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have discovered a possible secret to dramatically boosting the efficiency of perovskite solar cells hidden in the nanoscale peaks and valleys of the crystalline material.
Solar cells made from compounds that have the crystal structure of the mineral perovskite have captured scientists' imaginations. They're inexpensive and easy to fabricate, like organic solar cells. Even more intriguing, the efficiency at which perovskite solar cells convert photons to electricity has increased more rapidly than any other material to date, starting at three percent in 2009 -- when researchers first began exploring the material's photovoltaic capabilities -- to 22 percent today. This is in the ballpark of the efficiency of silicon solar cells.
>> Read the Full Article

What does the “city of the future” look like?
In an era of rapid technological advancement and increasing urbanization, it’s a fair question. Eighty percent of the U.S. population already lives in large cities* – each with a smartphone, wearable or other device in hand.
As such, city officials are beginning to piece together how those bits of technology can connect with assets like energy meters, garbage cans, street lights, traffic lights, water pipes and more. But, how do we make it all work together? By building a truly smart city.
A truly smart city is one with seamless connectivity that solves local problems and provides its inhabitants with safety, cleanliness and the most efficient ways to get from Point A to Point B. It’s a city that optimizes how we use valuable resources to help improve quality of life, positively impact our planet and open new economic opportunities. A truly smart city provides tremendous opportunities for its citizens and beyond.
>> Read the Full Article

Paris was at the forefront of public bike-sharing schemes, and it now has electric car-sharing schemes and is something of a laboratory for mobility. As of today, motorists with cars built before 1997, and motorcycles built before 2000, will no longer be able to drive them in the city during daylight hours on weekdays.
Paris Mayor Anne Hidalgo says keeping old cars out of the city will help lower pollution levels. But not everyone is happy about it.
Marc Vernhet makes his living driving tourists around Paris in the classic French car known as the Deux Chevaux, or two-horse power. Peugeot Citroen no longer makes the model, but for collectors, it's a nostalgic symbol of the good old days. Vernhet says tourists from all over the world want to ride in them.
>> Read the Full Article

Engineers at Oregon State University have created a new computer modeling package that people anywhere in the world could use to assess the potential of a stream for small-scale, “run of river” hydropower, an option to produce electricity that’s of special importance in the developing world.
The system is easy to use; does not require data that is often unavailable in foreign countries or remote locations; and can consider hydropower potential not only now, but in the future as projected changes in climate and stream runoff occur.
>> Read the Full Article

There was a period during the last ice age when temperatures in the Northern Hemisphere went on a rollercoaster ride, plummeting and then rising again every 1,500 years or so. Those abrupt climate changes wreaked havoc on ecosystems, but their cause has been something of a mystery. New evidence published this week in the leading journal Science shows for the first time that the ocean's overturning circulation slowed during every one of those temperature plunges - at times almost stopping.
"People have long supposed this link between overturning circulation and these abrupt climate events. This evidence implicates the ocean," said L. Gene Henry, the lead author of the study and a graduate student at Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory.
>> Read the Full Article
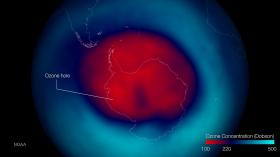
Scientists at MIT and elsewhere have identified the "first fingerprints of healing" of the Antarctic ozone layer, published today in the journal Science.
The team found that the September ozone hole has shrunk by more than 4 million square kilometers -- about half the area of the contiguous United States -- since 2000, when ozone depletion was at its peak. The team also showed for the first time that this recovery has slowed somewhat at times, due to the effects of volcanic eruptions from year to year. Overall, however, the ozone hole appears to be on a healing path.
The authors used "fingerprints" of the ozone changes with season and altitude to attribute the ozone's recovery to the continuing decline of atmospheric chlorine originating from chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). These chemical compounds were once emitted by dry cleaning processes, old refrigerators, and aerosols such as hairspray. In 1987, virtually every country in the world signed on to the Montreal Protocol in a concerted effort to ban the use of CFCs and repair the ozone hole.
>> Read the Full Article

Most animal lovers wouldn’t dream of harming an animal for fashion. Fur? No, thank you. Leather? I don’t think so. Yet they might be unknowingly killing sharks — and highly endangered kinds on top of that — for their beauty routine.
Unbeknownst to most, one little ingredient in products like sunscreens, moisturizing lotions, lip balms, lipsticks and face creams is responsible for the death of over three million sharks annually.
Killer ingredient
“Squalene is a naturally occurring compound found in large quantities in the liver of sharks,” explains the shark protection group Shark Trust. “A sharks’ large oily liver helps to control its position in the water column, however many cosmetics companies use the oil (and an associated compound called squalane) as a base for their moisturizing and skin care creams, lipstick and gloss, as it is non-greasy and softens skin.”
>> Read the Full Article

Rising sea-levels linked to global warming could pose a significant threat to the effectiveness of the world's peatland areas as carbon sinks, a new study has shown.
The pioneering new study, carried out by Geographers at the University of Exeter, examined the impact that salt found in sea water has on how successfully peatland ecosystems accumulate carbon from the atmosphere.
The researchers studied an area of blanket bog - a peat bog that forms in cool regions susceptible to high rainfall - at Kentra Moss, in Northwest Scotland.
>> Read the Full Article

A new twist on the use of renewable energy is saving children's lives in Africa. The innovation--a solar powered oxygen delivery system--is providing concentrated oxygen in hospital for children suffering from severe pneumonia.
The device created by Dr. Michael Hawkes, an assistant professor in the University of Alberta's Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, is the focus of a recently published study in The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease and is already in use in two hospitals in Uganda.
"Solar-powered oxygen is using freely available resources--the sun and air--to treat children with pneumonia in the most remote settings," says Hawkes. "It's very gratifying for a pediatrician doing research in a lower-resource setting to fill a clinical gap and save lives. It's what our work is all about."
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment