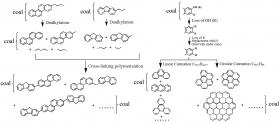
The organic matter in coal contains polycyclic aromatic compounds (PACs) of varying quantities in diverse soluble and insoluble forms. PACs in coal are of special interest for organic geochemical studies as they have been successfully used as biological marker compounds (biomarkers) and indicators of thermal maturity.
However, challenges exist when applying PACs in understanding the organic geochemistry of coal. For example, what are the sources of PACs in coals? How do they transform during the long-term coal-formation history? Is there any regular relationship between the PAC and macro-molecular structural changes?
>> Read the Full Article

The giant slug Limax maximus is native to Europe and Asia Minor but has spread widely, being found in North America, South America, North Africa, South Africa, Australia, New Zealand and other regions. The slug is recognized as a notorious pest because it eats agricultural and garden crops.
>> Read the Full Article

Small mountain glaciers play a big role in recharging vital aquifers and in keeping rivers flowing during the winter, according to a new study published in Geophysical Research Letters, a journal of the American Geophysical Union.
The study also suggests that the accelerated melting of mountain glaciers in recent decades may explain a phenomenon that has long puzzled scientists — why Arctic and sub-Arctic rivers have increased their water flow during the winter even without a correlative increase in rain or snowfall.
>> Read the Full Article
Time is of the essence when treating a patient undergoing a heart attack. Cardiac surgeons attempt to quickly stabilize the heart by applying reperfusion, a technique that restores oxygen to the heart by opening up blocked vessels with balloons and stents. While reperfusion can restore cardiac function, such sudden infusions of oxygen can also further injure severely depleted regions of the heart.
“It’s a double-edged sword,” says Anthony McDougal, a graduate student in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering. “The rapid return of oxygen is necessary for the heart to survive, but it could also overwhelm the heart.”
>> Read the Full Article

From indoor lighting to outdoor street lamps, our world is made brighter by artificial light. But the light that we perceive to be constant, actually fluctuates.
A University of Toronto computer scientist and researchers from the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology are studying electrical grids for cities, creating a camera that records the city's lights at a slower speed to get more accurate readings of changing voltages at particular locations.
>> Read the Full Article

Monsoon season now brings more extreme wind and rain to central and southwestern Arizona than in the past, according to new research led by the University of Arizona.
Although there are now fewer storms, the largest monsoon thunderstorms bring heavier rain and stronger winds than did the monsoon storms of 60 years ago, the scientists report.
>> Read the Full Article

Imagine rescuers searching for people in the rubble of a collapsed building. Instead of digging through the debris by hand or having dogs sniff for signs of life, they bring out a small, air-tight cylinder. They place the device at the entrance of the debris and flip a switch. From one end of the cylinder, a tendril extends into the mass of stones and dirt, like a fast-climbing vine. A camera at the tip of the tendril gives rescuers a view of the otherwise unreachable places beneath the rubble.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment