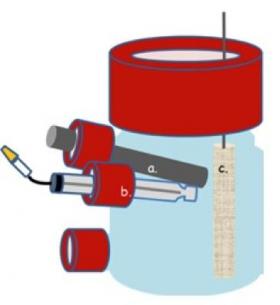
Warm and salty wastewater is a by-product of many industries, including oil and gas production, seafood processing and textile dyeing. KAUST researchers are exploring ways to detoxify such wastewater while simultaneously generating electricity. They are using bacteria with remarkable properties: the ability to transfer electrons outside their cells (exoelectrogenes) and the capacity to withstand extremes of temperature and salinity (extremophiles).
>> Read the Full Article

Catastrophic flooding from Hurricane Harvey that led to more than 60 deaths and thousands of rescues showed again that an accurate NOAA forecast by itself is not enough to ensure people grasp the risks and make sound decisions that save lives and property.
A new report released today by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine offsite linkconcludes that realizing the greatest return on investment from significant improvements in weather information will require a better understanding of how individuals, households and communities respond to weather forecasts, watches and warnings.
>> Read the Full Article

Researchers at the University of British Columbia have developed a new early warning system to predict when and where human-caused wildfires are most likely to occur in the spring.
Using satellite images of vegetation, the researchers can forecast where wildfire risk peaks in boreal forests by tracking moisture in fuel sources like leaves.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment