
Researchers are investigating a new material that might help in nuclear fuel recycling and waste reduction by capturing certain gases released during reprocessing. Conventional technologies to remove these radioactive gases operate at extremely low, energy-intensive temperatures. By working at ambient temperature, the new material has the potential to save energy, make reprocessing cleaner and less expensive. The reclaimed materials can also be reused commercially.
>> Read the Full Article

A new report by the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) and Interpol has highlighted the sophistication and growth of environmental crimes across the world. These crimes range from the illegal trade of wildlife, illegal mining, illegal forestry and fishing. And despite our growing global attention towards conservation, these crimes have jumped 26 percent in the past two years alone.
The report highlights the criminal fluidity of these trades. They say that transnational crime rings are no longer focusing on just one flow of illicit trade; rather, “criminals coordinate, evade or even shift their focus from drugs, human trafficking, counterfeit products and arms to any new opportunity – hazardous waste and chemicals, forest products, pangolins, giant clams, minerals and illegally extracted gold.”
According to the UNEP, the reasons behind this rise is linked to both increasing demand, primarily in Asia, as well as poverty in the regions where the smuggling of these goods take place. Local wildlife authorities across Africa, which often scrape by on a minimal budget, must constantly adapt to new methods and new extremes employed by poachers.
>> Read the Full Article

Fish: charming, but not terribly bright, right? That’s been the party line for years, but it turns out that it’s not quite accurate.
Some fish actually use tools, and as researcher Culum Brown points out, the lack of studies on fish populations means that we don’t actually know the extent this skill. Opening our eyes a little might reveal some fascinating new information about creatures we’ve traditionally identified as sitting at the lowest rung of animal life — even some vegetarians don’t see a conflict with including fish in their diets!
The first documented instance of tool use by a fish occurred in 2011, when a diver noticed a blackspot tuskfish doing something odd as he drifted along the Great Barrier Reef. When the diver investigated, he found that the fish was using a rock to crack open clam shells in order to access the meat inside. It showed a degree of resourcefulness that researchers hadn’t expected to see in fish — and it wasn’t the only intelligent tuskfish behavior.
>> Read the Full Article
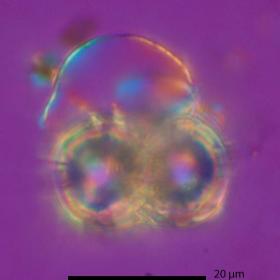
The number of species that can exist on Earth depends on how the environment changes, according to new research led by the University of Southampton.
By analysing the fossil record of microscopic aquatic creatures called planktonic foraminifera, whose fossil remains now resemble miniaturised popcorn and date back millions of years, the research provided the first statistical evidence that environmental changes put a cap on species richness.
>> Read the Full Article

Thousands of people spoke out this week to ask for more protection for a highly endangered and beloved population of orcas, otherwise known as the Southern Resident killer whales who live in the Pacific Northwest.
Thanks to whale watching tours, and organizations like the Orca Network and Center for Whale Research, which keeps an official census of their population, we have had the opportunity to glimpse into their daily lives. We’ve been able to celebrate births, mourn deaths and root for the elders among them, like Granny, who has been around long enough to see how drastically our actions have changed their home and families.
>> Read the Full Article

Daily Arctic sea ice extents for May 2016 tracked two to four weeks ahead of levels seen in 2012, which had the lowest September extent in the satellite record. Current sea ice extent numbers are tentative due to the preliminary nature of the DMSP F-18 satellite data, but are supported by other data sources. An unusually early retreat of sea ice in the Beaufort Sea and pulses of warm air entering the Arctic from eastern Siberia and northernmost Europe are in part driving below-average ice conditions. Snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere was the lowest in fifty years for April and the fourth lowest for May. Antarctic sea ice extent grew slowly during the austral autumn and was below average for most of May.
>> Read the Full Article

If the U.S. healthcare system were a country, it would rank 13th in the world for greenhouse gas emissions, according to new research. The study, published June 9 in PLOS ONE, quantified previously unreported environmental and public health impacts of the nation's healthcare sector.
>> Read the Full Article

An international team of scientists have found a potentially viable way to remove anthropogenic (caused or influenced by humans) carbon dioxide emissions from the atmosphere - turn it into rock.
The study, published today in Science, has shown for the first time that the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) can be permanently and rapidly locked away from the atmosphere, by injecting it into volcanic bedrock. The CO2 reacts with the surrounding rock, forming environmentally benign minerals.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment