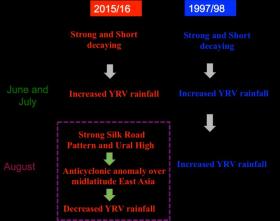
It is widely recognized that rainfall over the Yangtze River valley (YRV) strengthens considerably during the decaying summer of El Niño, as demonstrated by the catastrophic flooding suffered in the summer of 1998. Nevertheless, the rainfall over the YRV in the summer of 2016 was much weaker than that in 1998, despite the intensity of the 2016 El Niño having been as strong as that in 1998. A group of scientists from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, have now revealed the remarkable role played by the mid-latitude circulation in this surprising feature.
>> Read the Full Article

People who handle paper receipts regularly may be at increased risk for exposure to a chemical linked to breast and prostate cancers, according to new UAlberta research.
“We found that people who handled receipts printed on thermal paper containing the chemical had it lingering in their body for a week or more,” said Jiaying Liu, a PhD candidate in UAlberta’s Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology.
>> Read the Full Article

As 3-D printing has become a mainstream technology, industry and academic researchers have been investigating printable structures that will fold themselves into useful three-dimensional shapes when heated or immersed in water.
In a paper appearing in the American Chemical Society’s journal Applied Materials and Interfaces, researchers from MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and colleagues report something new: a printable structure that begins to fold itself up as soon as it’s peeled off the printing platform.
>> Read the Full Article

Teenagers who try e-cigarettes double their risk for smoking tobacco cigarettes, according to a new study.
The study — from the University of Waterloo and the Wake Forest School of Medicine — found that students in grades seven to 12 who had tried an e-cigarette are 2.16 times more likely to be susceptible to cigarette smoking.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment