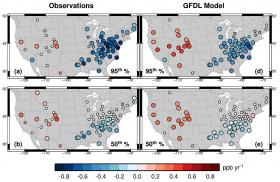
An influx of pollution from Asia in the western United States and more frequent heat waves in the eastern U.S. are responsible for the persistence of smog in these regions over the past quarter century despite laws curtailing the emission of smog-forming chemicals from automobile tailpipes and factories.
The study, led by researchers at Princeton University and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL), highlights the importance of maintaining domestic emission controls on cars, power plants and other industries at a time when pollution is increasingly global.
>> Read the Full Article
A tailored preventive oral health intervention significantly improved the cleanliness of teeth and dentures among elderly home care clients. In addition, functional ability and cognitive function were strongly associated with better oral hygiene, according to a new study from the University of Eastern Finland. The study is part of a larger intervention study, NutOrMed, and the findings were published in the Age and Aging journal.
>> Read the Full Article

A team of international researchers led by University of Freiburg hydrologist Dr. Andreas Hartmann suggests that inclusion of currently missing key hydrological processes in large-scale climate change impact models can significantly improve our estimates of water availability. The study shows that groundwater recharge estimates for 560 million people in karst regions in Europe, the Middle East and Northern Africa, are much higher than previously estimated from current large-scale models. The scientists have shown that model estimates based on entire continents up to now have greatly underestimated in places the amount of groundwater that is recharged from fractions of surface runoff. This finding suggests that more work is needed to ensure sufficient realism in large-scale hydrologic models before they can be reliably used for local water management. The team has published their research findings in the scientific journal “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).”
>> Read the Full Article

Jefferson Project researchers test effects of common road salt, additives, and alternatives
Organic additives found in road salt alternatives — such as those used in the commercial products GeoMelt and Magic Salt — act as a fertilizer to aquatic ecosystems, promoting the growth of algae and organisms that eat algae, according to new research published today in the Journal of Applied Ecology. Low levels of magnesium chloride — an alternative type of salt found in the commercial product Clear Lane – boost populations of amphipods, tiny crustaceans that feed on algae and serve as an important food source for fish.
>> Read the Full Article

Zika virus could be transmitted by more mosquito species than those currently known, according to a new predictive model created by ecologists at the University of Georgia and the Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies. Their findings, published today in the journal eLife, offer a list of 26 additional potential candidate species-including seven that occur in the continental United States-that the authors suggest should be the first priority for further research.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment