Renewable energy met more of Germany’s electricity needs than coal during the first six months of 2018 — the longest period that renewables have been the country’s largest source of energy to date. According to new data from the German Association of Energy and Water Industries (BDEW), 36.3 percent of Germany’s electricity was generated by solar, wind, hydropower, and biogas between January and June of this year, while coal provided only 35.1 percent.
Uncategorised
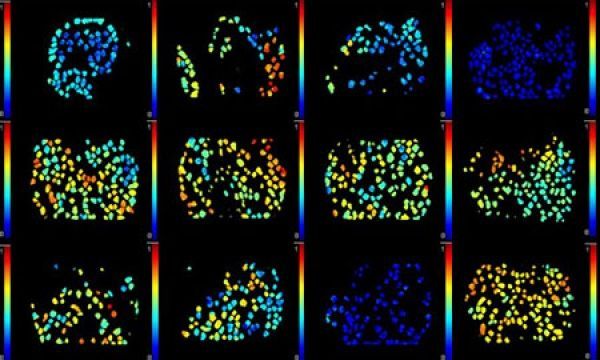
New method reveals how well cancer drugs hit their targets
Scientists have developed a technique that allows them to measure how well cancer drugs reach their targets inside the body. It shows individual cancer cells in a tumour in real time, revealing which cells interact with the drug and which cells the drug fails to reach.
In the future, the findings, published in Nature Communications, could help clinicians decide the best course and delivery of treatment for cancer patients.
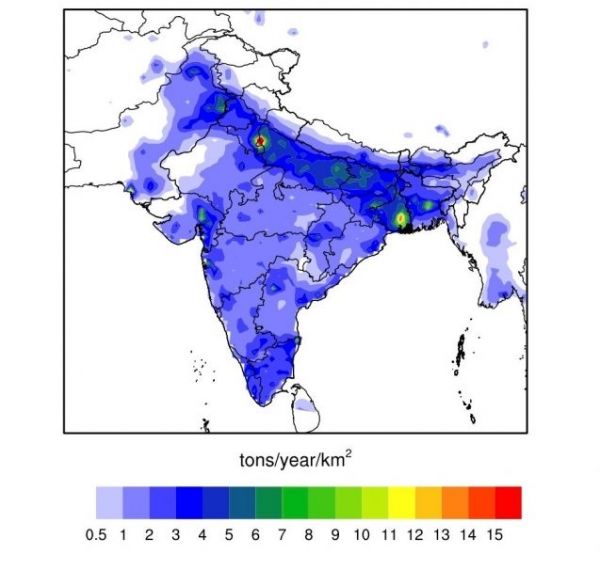
In India, Dirty Air Kills as Easily in the Country as in the City
A forthcoming study of northern India suggests that people living in rural areas are as likely to die prematurely from the effects of poor air quality as those living in cities. The study found that the sources of pollution in urban versus rural communities may be somewhat different, but the results are the same: high mortality linked to circulatory and respiratory problems. Air-pollution studies tend to focus on big cities, yet some 70 percent of India’s population dwells in rural areas, so the research may have wide implications.
Researchers use coal waste to create sustainable concrete
Washington State University researchers have created a sustainable alternative to traditional concrete using coal fly ash, a waste product of coal-based electricity generation.
The advance tackles two major environmental problems at once by making use of coal production waste and by significantly reducing the environmental impact of concrete production.
Xianming Shi, associate professor in WSU’s Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, and graduate student Gang Xu, have developed a strong, durable concrete that uses fly ash as a binder and eliminates the use of environmentally intensive cement. They report on their work in the August issue of the journal, Fuel.
Increasing Heat Is Driving Off Clouds That Dampen California Wildfires
Sunny California may be getting too sunny. Increasing summer temperatures brought on by a combination of intensifying urbanization and warming climate are driving off once common low-lying morning clouds in many southern coastal areas of the state, leading to increased risk of wildfires, says a new study.
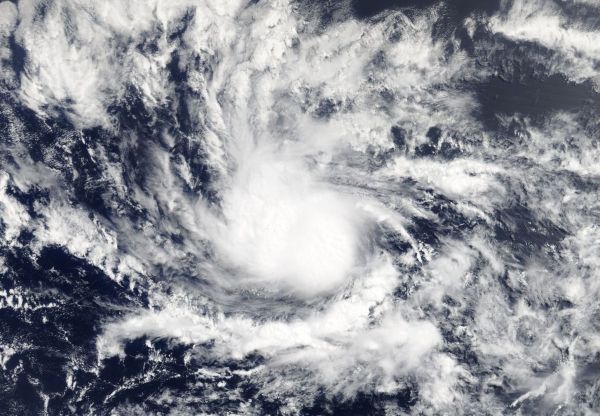
NASA's Terra Satellite Spots Second Atlantic Tropical Depression
The second tropical cyclone of the North Atlantic Hurricane season formed in the Central Atlantic Ocean and far from land. NASA's Terra satellite provided an early morning look at the small depression.