Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Exactly how fast this might occur is not clear. The capacity of terrestrial ecosystems to absorb carbon dioxide emissions from human activity may be greater than previously thought, according to a new study published in Nature Climate Change, which looks at how plants react to environmental change. The authors say these results improve our ability to look into the planet's future and predict the magnitude of climate change before it happens.
Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Exactly how fast this might occur is not clear. The capacity of terrestrial ecosystems to absorb carbon dioxide emissions from human activity may be greater than previously thought, according to a new study published in Nature Climate Change, which looks at how plants react to environmental change. The authors say these results improve our ability to look into the planet's future and predict the magnitude of climate change before it happens.
!ADVERTISEMENT!
The scientists from Imperial College London and University of York were investigating how changes in temperature and atmospheric carbon dioxide levels - such as those predicted under the effects of global climate change – may affect soil respiration and a plant's rate of growth, photosynthesis and respiration.
Carbon fixation is the removal of carbon dioxide from the air and its incorporation into solid compounds. Plants, algae, and many species of bacteria (cyanobacteria) fix carbon and create their own food by photosynthesis. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and water to produce sugars and occasionally other organic compounds, releasing oxygen as a waste product.
Plants can grow up to 50 percent faster in concentrations of 1,000 ppm CO2 when compared with ambient conditions, though this assumes no change in climate and no limitation on other nutrients. Previous research has shown that elevated CO2 levels can cause increased growth reflected in the harvestable yield of crops, with wheat, rice and soybean all showing increases in yield of 12–14% under elevated CO2.
The new research addresses a key question in environmental science about whether an increase in global temperatures will cause an increase or a decrease in the ability of ecosystems to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, a problem for which scientists do not yet have a convincing answer. Some scientists have suggested that increases in temperature will cause the release of greenhouse gases from ecosystems such as oceans and soils, possibly resulting in runaway climate change, where environmental change passes a tipping point. Others have suggested that an explosive growth of plants and algae will help to mop up excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Following the results of this study, the scientists conclude that, with the help of plants, the Earth’s terrestrial ecosystems may well have more capacity to buffer against runaway climate change than scientists previously thought.
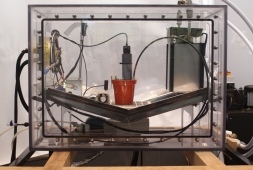
The scientists grew plants in sealed experimental cabinets, providing them with soil, light, water, and a controlled atmosphere that mimicked possible future temperatures and levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Over several months they measured how well the plants absorb carbon dioxide under these changing environmental conditions. They noted that the plants absorb a large proportion of additional carbon dioxide gas that was introduced to the cabinet, preventing the temperature from increasing more than 2.3ºC.
They observed this under the environmental conditions that match one of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) optimistic scenarios of man-made greenhouse emissions by 2100, in which the population rises to 9 billion in 2050 before declining, and efforts are made to reduce human effect on the environment.
Dr Alex Milcu from Imperial's Department of Life Sciences, who is the corresponding author of the research, said: "Experiments of this nature are key to accurately predicting the future levels of carbon dioxide and global temperatures. We are really improving our understanding of how plants react to global environmental changes, but a discrepancy exists between our results, those from open unsealed experiments, and data from the best computer simulations. Right now, the best way to improve these simulations is through more experimental work to understand the way that carbon cycles between soil, vegetation and the atmosphere."
Co-author Dr Martin Lukac, now based at the University of Reading, said: "Our results from the climate-controlled cabinets suggest the role plants have in cleaning up excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere may be pretty good, at least at lower levels of anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions. We do have to be cautious in scaling up the results from our sealed-cabinet experiments to the whole world, and probably would not expect to see such a strong effect in real ecosystems due to additional limiting factors such as nutrient and water availability."
For further information see Plant Uptake
Lab image via Imperial College.