Man-made phosphorus pollution is reaching dangerously high levels in freshwater basins around the world, according to new research.
articles
Mosquitoes Remember Human Smells, But Also Swats, Virginia Tech Researchers Find
Your grandmother’s insistence that you receive more bug bites because you’re ‘sweeter’ may not be that far-fetched after all, according to pioneering research from Virginia Tech scientists.
Ultrathin needle can deliver drugs directly to the brain
MIT researchers have devised a miniaturized system that can deliver tiny quantities of medicine to brain regions as small as 1 cubic millimeter. This type of targeted dosing could make it possible to treat diseases that affect very specific brain circuits, without interfering with the normal function of the rest of the brain, the researchers say.
Repurposed Drug Found to be Effective Against Zika Virus
In both cell cultures and mouse models, a drug used to treat Hepatitis C effectively protected and rescued neural cells infected by the Zika virus — and blocked transmission of the virus to mouse fetuses.
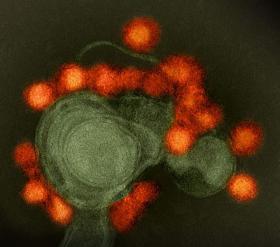
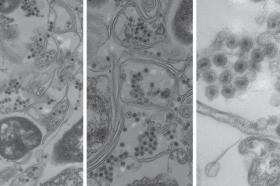
New type of virus found in the ocean
A type of virus that dominates water samples taken from the world’s oceans has long escaped analysis because it has characteristics that standard tests can’t detect. However, researchers at MIT and the Albert Einstein College of Medicine have now managed to isolate and study representatives of these elusive viruses, which provide a key missing link in virus evolution and play an important role in regulating bacterial populations, as a new study reports.
Missing in Action
Once abundant in Southern California, the foothill yellow-legged frog inexplicably vanished from the region sometime between the late 1960s and early 1970s. The reasons behind its rapid extinction have been an ecological mystery.