The majority of people who are touched by an epileptic seizure event can only endure the terrifying moments and put their faith in doctors to help their loved one. The University of Lethbridge’s Dr. Artur Luczak, however, was in a position to do much more when his infant son suffered a seizure, and what he’s learned about seizures since has flipped the script on understanding how the brain functions during these traumatic events.
articles
Long-term weather forecasting a guessing game
Famous for its weather forecasts, the Old Farmer’s Almanac has published its predictions for the coming year—but don’t believe everything you read.
The folksy pocket-sized magazine has been a regular go-to for farmers and other fans during fall harvest season since it first began publishing in 1792. As cosy and comforting as pumpkin pie, it offers everything from home remedies to food recipes—but the long-range weather predictions that fill many of its pages are nothing but pure guesswork, said a University of Alberta weather modelling expert.
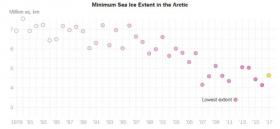
Arctic sea ice at minimum extent for 2017
Arctic sea ice extent has likely reached its minimum extent for the year, at 4.64 million square kilometers (1.79 million square miles) on September 13, 2017, according to a team of international scientists. The 2017 minimum is the eighth lowest in the 38-year satellite record. The Arctic sea ice minimum marks the day – typically in mid-September – when sea ice reaches its smallest extent at the end of the summer melt season.
Energy technologies get a boost toward commercial use
Six energy technologies that do everything from protect fish to monitor the health of flow batteries are getting a boost at the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
DOE is awarding PNNL nearly $1.5 million to bring six technologies closer to commercial use. The projects were announced today by DOE's Office of Technology Transitions, which selected them for funding from its Technology Commercialization Fund. The technologies show great promise, but need further development to improve their potential use in commercial products or services.
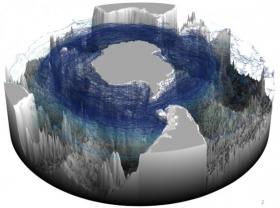
Deep waters spiral upward around Antarctica
Since Captain James Cook’s discovery in the 1770s that water encompassed the Earth’s southern latitudes, oceanographers have been studying the Southern Ocean, its physics, and how it interacts with global water circulation and the climate.
Brain cancer growth halted by absence of protein
The growth of certain aggressive brain tumors can be halted by cutting off their access to a signaling molecule produced by the brain’s nerve cells, according to a new study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine.