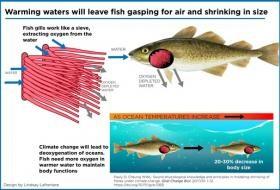
Se espera que los peces disminuyan en tamaño entre un 20 y un 30 por ciento si la temperatura del océano continúa subiendo debido al cambio climático. Un nuevo estudio realizado por investigadores de la Universidad de Columbia Británica proporciona una explicación más profunda de por qué se espera que los peces disminuyan de tamaño.
articles
Hatching an idea
Backyard chickens are permitted in a number of Canadian cities, including Vancouver, Victoria, Whitehorse and some boroughs of Montréal.
Wanda Martin would like to see Saskatoon on that list.
Historic Legacies Affect Climate Change Survival In Caribbean
The legacies of empire have increased the vulnerability of Caribbean states to climate change, according to University of Warwick expert Dr Leon Sealey-Huggins.
Pipeline pain relief on horizon with spill-resistant bitumen
Ian Gates describes each pebble of bitumen as resembling a liquid-filled headache capsule and, for an Alberta struggling to build pipelines, this tiny package could spell pain relief indeed.
Freshly patented and weeks away from pilot-scale production, the professor’s revolutionary heavy oil and bitumen pellets may finally provide a pipeline-free solution to getting Alberta’s largest oil reserves to market in a cheap, sustainable manner, while vastly reducing the environmental risk of transportation.
Cancer Survivors Who Quit Smoking Sooner Can Live Longer
Lung cancer survivors who quit smoking within a year of diagnosis will live for longer than those who continue to smoke, according to new research led by the Universities of Oxford and Birmingham.
"Keep it local" approach to protecting the rainforest can be more effective than government schemes
Conservation initiatives led by local and indigenous groups can be just as effective as schemes led by government, according to new research.