Animal carnivores living in and around human habitation are declining at an unprecedented rate – but they may provide crucial benefits to human societies.
articles
Climate Change Affects Fish Reproductive Phenology in Plateau Area: Study
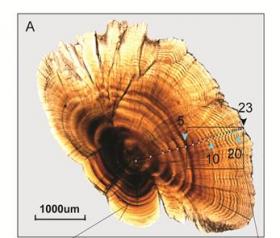
Climate change has threatened the global environment and biodiversity, particularly the aquatic ecosystems as well as the development of human ecosociety. The Tibetan Plateau is the region possessing the richest water resources in Asia but highly affected by the global climate change.
Crop Failure in the Andes
Kenneth Feeley, the Smathers Chair of Tropical Tree Biology in the University of Miami’s Department of Biology, is an expert in studying the effects of climate change on tropical forests. From the mountains of Peru to the lowlands of the Amazon, Feeley examines the ramifications of climate change on the trees and other species that comprise the diverse forests of these regions. Yet, recently, Feeley shifted gears from studying tropical forests to examining the impacts of climate change in rural farming communities in Peru.
Mining weather data from Civil War-era Navy logbooks
A new grant will let a University of Washington-based project add a new fleet to its quest to learn more about past climate from the records of long-gone mariners. The UW is among the winners of the 2017 “Digitizing Hidden Special Collections and Archives” awards, announced earlier this month by the Washington, D.C.-based Council on Library and Information Resources.
Fox Creek Quakes Linked to Volume and Location of Hydraulic Fracturing
The volume of hydraulic fracturing fluid and the location of well pads control the occurrence and frequency of measurable earthquakes, new research from the Alberta Geological Survey and the University of Alberta shows.
USGS Scientist Mobilizes with Recon Team to Learn from Mexico's Earthquake Early Warning System
A few weeks after a magnitude-7.1 earthquake struck central Mexico on Sept. 19, 2017 — leaving hundreds dead and dozens of buildings destroyed — USGS seismologist Elizabeth Cochran and a team of experts mobilized to Mexico City to assess the performance of the Mexico Seismic Warning System (Sistema de Alerta Sísmica Mexicano or SASMEX) and the public’s perception of the alerts.